-
Product Name
Cynomolgus CD166/ALCAM (Fc Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM)/Cluster of differentiation (CD166) is a type I transmembrane cell adhesion molecule belonging to the Ig superfamily and a ligand for CD6 that is expressed on T lymphocytes. The extracellular domain of ALCAM contains five Ig-like domains (three Ig-like C2-type domains and two Ig-like V-type domains), of which the amino-terminal V1 domain is essential for ligand binding and ALCAM-mediated cell aggregation. ALCAM mediates both heterophilic (ALCAM-CD6) and homophilic (ALCAM-ALCAM) cell-cell interactions. ALCAM/CD6 interaction plays a role in T cell development and T cell regulation, as well as in the binding of T- and B-cells to activated leukocytes. Recently, homophilic (ALCAM-ALCAM) adhesion was shown to play important roles in tight cell-to-cell interaction and regulation of stem cell differentiation. While expressed in a wide variety of tissues, ALCAM is usually restricted to subsets of cells involved in dynamic growth and/or migration, including neural development, branching organ development, hematopoiesis, immune response and tumor progression. And CD166 is regarded as a potential novel breast cancer indicator and therapeutic target.
-
Protein name
CD166 antigen isoform 1
-
Protein short names
DM-GRASP; MUSC; BEN; AI853494; CD166; MGC27910; MEMD; ALCAM; SC1
-
Uniprot ID
H9ERZ1
-
Gene Name
ALCAM
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus ALCAM (NP_001244631.1) (Met1-Ala526) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Cynomolgus
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant cynomolgus ALCAM consists 740 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 82.9 kDa.
-
Purity
> 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
Validations
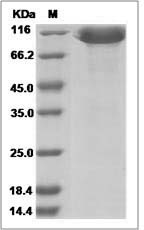
Cynomolgus CD166 / ALCAM Protein (Fc Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
