PepBox – Automatic Quote Tool
Please do not include peptide end modifications (N-terminal or C-terminal)
To input peptide sequence, please input abbreviations for common amino acids, for unusual amino acids and modified amino acids, use 3 letters abbreviation in the middle of "{ }", e.g. D-Phenylalanine: {D-Phe}, phosphorylated Serine: {pSer}, methylated Arginine: {Arg(me)}, methylated Lysine: {Lys(Me)}, dimethylated Lysine: {Lys(Me2)}, trimethylated Lysine: {Lys(Me3)}.
For cases that do not working properly of PepBox, please directly contact us.
Guide of peptide purity requirements for experiments.
Large-scale projects or special project, please contact our senior account manager.
Visit our Peptide Property Calculator tool.
|
If the modification is not listed here, please contact us directly. |
|
|
If the modification is not listed here, please contact us directly. |
|
| Diffcult peptides may subject to extra costs, such as peptides rich of cysteines or hydrophobic amio acids. | |
You could find the full list of modifications here
D form normal amino acids:
- {D-Ala}
- {D-Arg}
- {D-Asp}
- {D-Asn}
- {D-Cys}
- {D-Glu}
- {D-Gln}
- {D-His}
- {D-Ile}
- {D-Allo-Ile}
- {D-Leu}
- {D-Lys}
- {D-Met}
- {D-Pro}
- {D-Phe}
- {D-Ser}
- {D-Tyr}
- {D-Thr}
- {D-Trp}
- {D-Val}
Methyl amino acids:
- {Arg(Me)}
- {Arg(Me)2-symmetrical}
- {Arg(Me)2-asymmetrical}
- {Tyr(Me)}
- {Thr(Me)}
- {Ser(Me)}
- {Lys(Me)}
- {Lys(Me2)}
- {Lys(Me3)}
Phosphorylation:
- {pSer}
- {pTyr}
- {pThr}
- {D-pSer}
- {D-pTyr}
- {D-pThr}
Others:
Tips for improving enzymatic and chemical stability of peptides
Cyclisation: head to tail, head/tail to side chain or side chain to side chain(eg peptide stapling)
Moving away from proteinogenic amino acids: incorporate D-amino acids
Slowing down renal clearance by chemical modifications: N-acetylation, C-amidation, N-Methylation of amide bonds, polyethylene glycol (PEG) modification, incorporation of RGD peptide, addition of fatty chains
Enhancing bioavailability via formulations: include permeation enhancers and acid-stable coatings
Removal of TFA salt
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is a strong acid, which is commonly used to cleave synthesized peptides from solid-phase resins and is also used to improve HPLC performance in the peptide purification step. By default, custom peptides are delivered as lyophilized TFA salts, and can contain as much as 10-45% TFA.
TFA in custom peptides can cause inexplicable discrepancies in subsequent assay data. For instance, TFA in nM concentrations has been shown to interfere with cellular assays, inhibiting cellular proliferation in some instances, and increasing cell viability in others. It has also been found to be an unintended allosteric modulator of the glycine receptor, GlyR.
TFA Removal Service is recommended for:
- Peptides that will be used in cellular assays
- Peptides that will be used as APIs or in manufactured products
- For hydrophilic peptides containing numerous basic residues
The most adapted method is to replace TFA counterions by an stronger acid such as hydrochloric acid (HCl). Exchanging TFA to acetate is also commonly used.
A Reliable supplier of high-quality synthetic peptide.
NovoPro has been providing reliable custom peptides synthesis services for 1000+ scientists worldwide for 4 years. It is our ultimate goal to help you obtain better results in a shorter time while saving you money. Please find publications citing NovoPro peptides.
-
Impossible is nothing
*As long as 200aa, from mg to kg
*Any sequence, any length, any complexity
* Comprehensive modifications
-
Highest Quality
*>95% peptide synthesis success rate
*Up to 98% purity of peptide
-
Rigid Quality Control
*Detailed QC reports of MS, HPLC and COA documents
*Comprehensive quality assurement procedures
-
One-click Quote
Most convenient Pepbox for automatic peptide analysis and quote
Enjoying your ordering
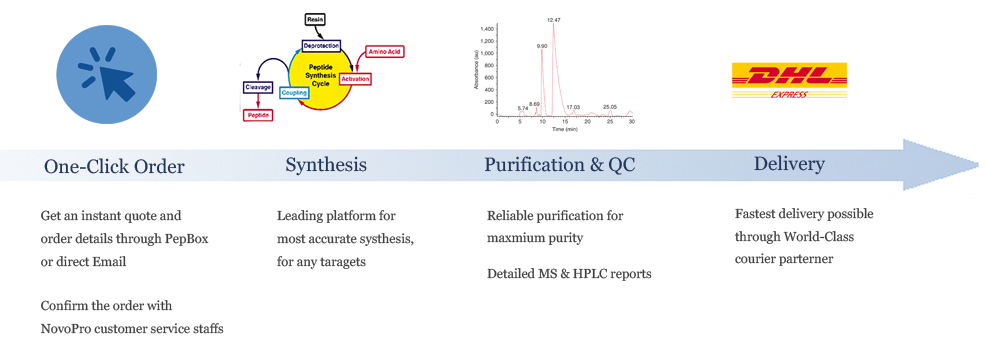
Ordering Processes
List Price
|
List Price* per amino acid for Peptide of 1-30 amino acids (5 mg)
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purity | Crude | Desalt | >75% | >90% | >95% |
| Price | $2.06 | $4.29 | $6.00 | $7.03 | $10.46 |
* Additional discounts will be applied for large-scale peptide synthesis orders.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
- 1. How may I place my order?
-
Answer
NovoPro needs the sequence, desired purity, desired quantity, and preferred payment information. If you have a PO (Purchase Order) number or credit card, you can place the order directly online using our secure server. Alternatively, you can send us the sequence by email and fax us the PO. If you like, you may use our PepBox – Automatic Quote Tool for all peptide orders up to 100 mg.
- 2. What is the typical turnaround time for peptide synthesis at NovoPro?
-
Answer
Our typical turnaround time is about three weeks. The turnaround time may vary depending on the peptide length and complexity of synthesis. The regular short peptide <20 aa only take 1-2 weeks.
- 3. How much does it cost to ship a peptide to the US or EU?
-
Answer
We ship our products to many countries. The overseas shipping charge is $39 per shipment for most countries.
- 4. What kinds of payment do you accept?
-
Answer
NovoPro accepts credit cards (Visa, MasterCard, American Express), checks, and wire transfers. For orders, you may send us a PO (Purchase Order). For certain orders, NovoPro may require a deposit.
- 5. How do you ship peptides? What data will be provided?
-
Answer
All peptides will be lyophilized and shipped in small microcentrifuge tubes (2 ml). Large amounts of peptide may be aliquoted into several tubes. For every single peptide, data sheets containing information such as amino acid sequence, modifications, purity, mass spectrum (MS) data, and HPLC data will be provided.
- 6. What is peptide purity?
-
Answer
The purity of NovoPro’s catalog peptides is usually about 95%, up to 99% purity. This means that 95% of the NET PEPTIDE content (but not total peptide content, see question 10) of the dry powder shipped to you is composed of your target peptide. The other 5% of the PEPTIDE material in your sample is usually composed of the so-called deletion sequences that sometimes co-purify with the target peptide. Deletion sequences are generated during peptide synthesis, when due to the slight inefficiencies of the coupling reaction some amino acids are skipped in some of the synthesized molecules. Purity is usually determined by reverse-phase HPLC.
- 7. How pure does my peptide need to be?
-
Answer
That depends on your specific application. NovoPro can synthesize peptides to 98% purity. Here is a general guideline for peptide purity requirements:
Purity Application >85% Immunological applications and polyclonal antibody production >90% SAR studies, bioassays >95% In vitro bioassays such as ELISA, enzymology, biological activity >98% NMR, crystallography, sensitive bioassays - 8. What methods do you use to purify the peptide?
-
Answer
HPLC is used for purification.
- 9. What is net peptide content?
-
Answer
It is important to understand the difference between net peptide content and total peptide content. The dry peptide powder shipped to you usually contains not only peptide, but also some other substances such as water, absorbed solvents, counter ions and salts. The total peptide content refers to the weight of this mixture. Net peptide weight indicates the actual weight of the peptide component of your sample. Net peptide content is usually 50-80% of the total peptide weight (also called gross peptide weight) and is usually determined by amino acid analysis or UV spectrophotometry. Net peptide content should not be confused with purity. Purity defines the percentage of the target peptide sequence in the peptide component of your sample.
- 10. How do you calculate theoretical net peptide content?
-
Answer
Theoretical net peptide content (calculated assuming that counterions are the only non-peptide components present in your peptide sample) can be estimated by dividing molecular weight of the peptide by a sum of this molecular weight and a number of trifluoroacetate counterions that are required to neutralize the peptide multiplied by the molecular weight of the TFA counterion (MW= 114). For example, a synthetic peptide of MW=1000 with a free N-terminal amino group and one Arg has theoretical net peptide content of 1000/(1000 + 2 x 114 ) = 1000/1228 =0.81 or 81%. In practice, counterions are not the only possible contaminants in the peptide sample. It can also contain water, absorbed solvents and traces of other substances. As a result, the actual net peptide content is usually determined by quantitative amino acid analysis.
- 11. How should I store the peptides?
-
Answer
Lyophilized peptides can be stored long-term at -20°C. For shor-term, you may store it at 4°C.
- 12. What is the best way to dissolve the peptide?
-
Answer
The solubility of given peptides varies depending on their amino acid sequences and modifications. NovoPro purifies peptides by HPLC using a water and acetonitrile gradient. Here are some general tips for dissolving peptides:
- Sonication will increase solubility.
- 10% acetic acid in the solvent will help dissolve basic peptides.
- 10% ammonium bicarbonate will help dissolve acidic peptides.
- For peptides with extremely low solubility in aqueous solutions, organic solvents (such as DMSO, isopropanol, methanol, and acetonitrile) should be used first. Once the peptides are completely dissolved, water may be gradually added until the desired concentration is obtained.
- 13. What is a counterion?
-
Answer
Most peptides except those that do not have basic amino acids such as Arg, Lys, His or those with blocked N-termini exist in the form of their salts. Synthetic peptides that are purified by HPLC are usually obtained as TFA salts. Their basic amino acid residues and N-termini are protonated and have trifluoroacetate (CF3COO -) counterions.
- 14. What methods do you use to synthesize peptides?
-
Answer
For peptides with fewer than 50 amino acids, we use stepwise SPPS chemical methods. For peptides with more than 50 amino acids, we use fragment condensation, native ligation or our proprietary recombinant methods.
- 15. What if some problem happens during the synthesis of my specific peptide?
-
Answer
Each peptide has its specific characteristics and not all outcomes can be anticipated. If something goes wrong during the synthesis and we cannot deliver your peptide on time, we will inform you as soon as possible.
- 16. What is the maximum peptide length you can produce?
-
Answer
NovoPro can synthesize peptides of length up to 200 aa. Peptides of 50-70 aa can be obtained by direct chemical synthesis. Longer peptides can be generated by chemically linking several synthetic peptide components. Proteins can also be chemically synthesized: learn more about NovoPro’s chemical protein synthesis service.
- 17. What quality control data is provided by NovoPro?
-
Answer
Quality assurance documentation provided with every NovoPro peptide includes mass spectral and HPLC analyses determining composition and purity. Amino acid analysis is available upon request. We also provide storage and handling guidelines.
- 18. In what direction are the peptides synthesized?
-
Answer
Peptides are synthesized from the C-terminus to the N-terminus of the sequence.
- 19. What are the applications of peptide libraries?
-
Answer
Peptide libraries are efficient tools for GPCR ligand screening, protein-protein interaction studies, functional proteomics, nucleic acid binding, enzyme substrate and inhibitor screening, antigen and epitope screening, peptide/protein cross-talk studies, the discovery of signal molecules, and other processes significant to modern drug discovery.
- 20. Can you provide cGMP-grade peptides?
-
Answer
NovoPro provides large-scale cGMP peptide services with capacity up to 2 kilograms per project. Our comprehensive experiences in cGMP-grade peptides synthesis for therapeutic and diagnostic applications give us an edge over the competition. We guarantee consistency, viability, and delivery.
- 21. Are there any requirements for phosphopeptide design?
-
Answer
We recommend that you position the phosphorylated residue no more than 10 residues away from the N-terminus because the coupling efficiency of residues following a phosphorylated residue is significantly reduced.
- 22. Are there any requirements for introducing dye modifications?
-
Answer
We recommend that you add a spacer between the peptide and the dye molecule. This will reduce the chance of the dye affecting peptide folding and binding to receptors. However, if the purpose of the dye labeling is to quantify fluorescence transfer between different structures spacers should not be introduced.
- 23. What is the advantage of capping the N and C termini of the peptide?
-
Answer
Capping will make peptide appear more like native protein. The N terminus can be capped with an acetyl group and C terminus with an amide group.
- 24. What are the advantages of PEGylation of peptides?
-
Answer
PEGylation adds poly (ethylene glycol) polymer to target molecules through covalent attachments. PEGylation effectively enhances the peptides’ therapeutic properties by masking them from the host’s immune system, increasing their solubility (for hydrophobic drugs) and bioavailability. It can also prolong the peptides circulatory time within the host through reduced renal clearance.
