-
Product Name
p38 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
p38 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in mouse heart tissue, rat heart tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 35 kDa,41 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
CSAID binding protein antibody; CSBP antibody; CSBP1 antibody; CSBP2 antibody; CSPB1 antibody; EXIP antibody; MAP kinase 14 antibody; MAP kinase MXI2 antibody; MAP kinase p38 alpha antibody; MAPK 14 antibody; MAPK14 antibody; MAX interacting protein 2 antibody; Mxi2 antibody; p38 antibody; p38ALPHA antibody; PRKM14 antibody; PRKM15 antibody; SAPK2A antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of p38 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_139012). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:2000
-
Validations
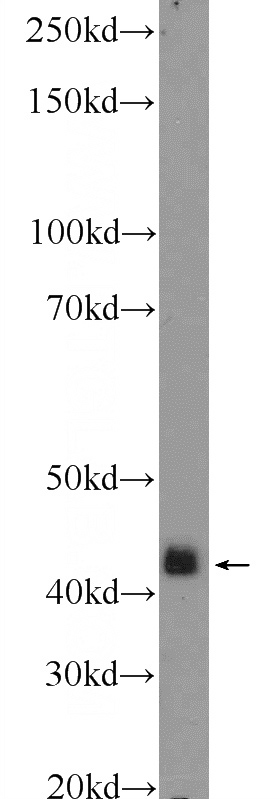
mouse heart tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:113549(p38 MAPK Antibody) at dilution of 1:600
-
Background
MAPK14(mitogen-activated protein kinase 14) is also named as SAPK2A, p38MAPK, CSBP1, RK, p38, EXIP, Mxi2, CSBP2, PRKM14, PRKM15, CSPB1, p38ALPHA and belongs to the MAP kinase subfamily. MAPK14-signaling is a central pathway for the integration of instructive signals in dendritic cells for T(H)17 differentiation and inflammation(PMID:22231518). It plays an important role in the regulation of hematopoietic stem cellself-renewal in vitro and inhibition of MAPK14 activation with a small molecule inhibitor may represent a novel approach to promote ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem cell(PMID:21198398). This protein has 4 isoforms produced by alternative splicing.
-
References
- Zheng S, Yang C, Liu T. Clinicopathological significance of p38β, p38γ, and p38δ and its biological roles in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine. 2015.
- Li X, Zou K, Gou J. Effect of baicalin-copper on the induction of apoptosis in human hepatoblastoma cancer HepG2 cells. Medical oncology (Northwood, London, England). 32(3):72. 2015.
- Zhang P, Feng S, Bai H. Polychlorinated biphenyl quinone induces endothelial barrier dysregulation by setting the cross talk between VE-cadherin, focal adhesion, and MAPK signaling. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology. 308(10):H1205-14. 2015.
- Su C, Xia X, Shi Q. Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone versus CCl₄-Induced Hepatic Injury through Different Mechanisms: The Implication of Free Radical Scavenging and Nrf2 Activation. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. 63(22):5468-75. 2015.
- Li J, Wang F, Xia Y. Astaxanthin Pretreatment Attenuates Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion-Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy via the ROS/MAPK Pathway in Mice. Marine drugs. 13(6):3368-87. 2015.
- Gu A, Jie Y, Sun L, Zhao S, E M, You Q. RhNRG-1β Protects the Myocardium against Irradiation-Induced Damage via the ErbB2-ERK-SIRT1 Signaling Pathway. PloS one. 10(9):e0137337. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
