-
Product Name
Anti-Phospho-p38 (Thr180/Tyr182) Rabbit antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Phospho-p38 (Thr180/Tyr182) Rabbit polyclonal antibody
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of threonine 180 or tyrosine 182 (E-M-T(p)-G-Y(p)-V-A) derived from Human P38 MAPK.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
Supplied at 1.0mg/mL in phosphate buffered saline (without Mg2+ and Ca2+), pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol.
-
Storage instructions
Store at 4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
-
Applications
WB:1/500-1/1000
-
Validations
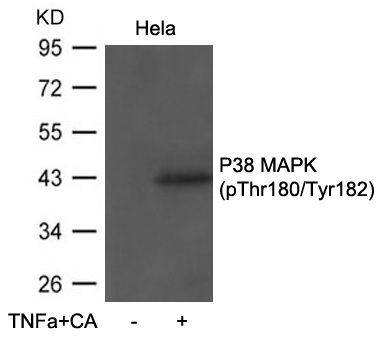
Western blot analysis of extracts from Hela cells untreated or treated with TNFu03b1+CA using P38 MAPK(Phospho-Thr180/Tyr182) Antibody .
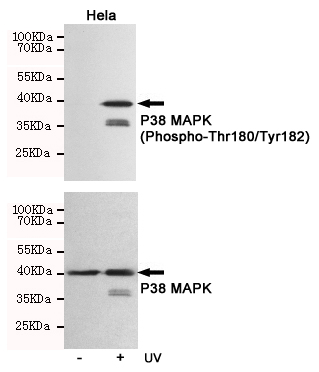
Western blot analysis of extracts from Hela cells, untreated or treated with UV, using P38 MAPK(Phospho-Thr180/Tyr182) Rabbit pAb (166717,1:500 diluted,upper) or p38 MAPK Rabbit pAb (310008,1:500 diluted,lower).
-
Background
Swiss-Prot Acc.Q16539.
-
References
- Selenoprotein X Gene Knockdown Aggravated H2O2-Induced Apoptosis in Liver LO2 CellsProtective Effect of Selenoprotein X Against Oxidative Stress-Induced Cell Apoptosis in Human Hepatocyte (LO2) Cells via the p38 Pathway
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
