-
Product Name
Human VEGF / VEGFA / VEGF165 recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), also known as vascular permeability factor (VPF) and VEGF-A, is a potent mediator of both angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in the fetus and adult. It is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family and often exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer. VEGF-A protein is a glycosylated mitogen that specifically acts on endothelial cells and has various effects, including mediating increased vascular permeability, inducing angiogenesis, vasculogenesis and endothelial cell growth, promoting cell migration, inhibiting apoptosis and tumor growth. VEGF-A protein is also a vasodilator that increases microvascular permeability, thus it was originally referred to as vascular permeability factor.
-
Protein name
Vascular endothelial growth factor A
-
Protein short names
RP1-261G23.1; VEGF; VPF; VEGF-A; MVCD1; MGC70609
-
Uniprot ID
P15692
-
Gene Name
VEGFA; VEGF
-
Source/Expression Host
Baculovirus-Insect Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the human VEGF 165 isoform (P15692-4) (Met1-Arg191) was expressed. Human and Cynomolgus VEGF165 sequences are identical.
-
Protein Species
Human
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant human VEGF consists of 165 amino acids after removal of the signal peptide and predicts a molecular mass of 19.2 kDa. Due to different glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhVEGF165 is approximately 20 and 22 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, corresponding to the monomer.
-
Purity
> 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Activity
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC).
The ED50 for this effect is typically 3-12 ng/ml. -
Validations
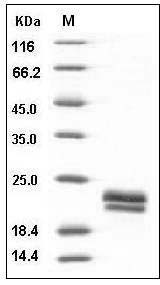
Human / Cynomolgus VEGF / VEGFA / VEGF165 Protein SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
