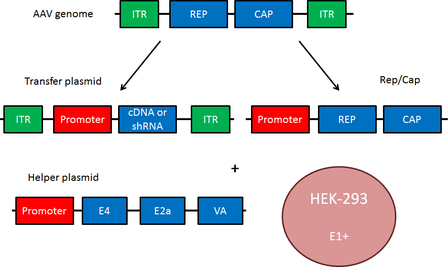
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is a replication-defective single-stranded DNA virus of the Parvoviridae family. Productive infection of AAV requires the presence of a helper virus, such as adenovirus (Ad) or herpes simplex virus(HSV). AAV has a genome size of 4.7 kb and encodes two types of protein: the Rep polypeptides involved in its replication and the capsid proteins used for its encapsidation. The AAV genes are flanked by two 145 base inverted terminal repeats (ITRs), which form a characteristic hairpin structure. Rep and Cap are translated to produce multiple distinct proteins (Rep78, Rep68, Rep52, Rep40 - required for the AAV life cycle; VP1, VP2, VP3 - capsid proteins). When constructing an AAV transfer plasmid, the transgene is placed between the two ITRs, and Rep and Cap are supplied in trans.
In addition to Rep and Cap, AAV requires a helper plasmid containing genes from adenovirus. These genes (E4, E2a and VA) mediate AAV replication. The transfer plasmid, Rep/Cap, and the helper plasmid are transfected into HEK293 cells, which contain the adenovirus gene E1, to produce infectious AAV particles.
A serotype refers to the subtype of microorganism that can be classified together based on their surface antigens. In the context of viruses, like AAV, serotype refers to the variation of the viral capsid proteins which dictate their antigenic properties. The AAV capsid is encoded by the cap gene consisting of the ORFs for the structural proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3; together 60 monomers of the structural proteins interact to form the AAV capsid.
The variation in the capsid proteins confers its differential ability to bind to different cellular receptors and thus, its specificity for certain cell types, tissues, and organs.
More than eleven serotypes of AAV have thus far been identified, with the best characterized and most commonly used being AAV2. These serotypes differ in their tropism, or the types of cells they infect, making AAV a very useful system for preferentially transducing specific cell types. The chart below gives a summary of the tropism of AAV serotypes, indicating the optimal serotype(s) for transduction of a given organ.
|
Tissue |
Optimal Serotype |
|
CNS |
AAV1, AAV2, AAV4, AAV5, AAV8, AAV9 |
|
Heart |
AAV1, AAV8, AAV9 |
|
Kidney |
AAV2 |
|
Liver |
AAV7, AAV8, AAV9 |
|
Lung |
AAV4, AAV5, AAV6, AAV9 |
|
Pancreas |
AAV8 |
|
Photoreceptor Cells |
AAV2, AAV5, AAV8 |
|
RPE (Retinal Pigment Epithelium) |
AAV1, AAV2, AAV4, AAV5, AAV8 |
|
Skeletal Muscle |
AAV1, AAV6, AAV7, AAV8, AAV9 |
When transfected into cells, AAV remain primarily episomal, while lentiviruses integrate into the genome. AAV can also integrate into the target cell genome at low frequency. Wild-type AAV integrates into the host genome at a specific site, AAVS1 on human chromosome 19. This site is favored due to the presence of a Rep binding element; however, random integrations may occur at a much lower frequency.
Researchers have further refined the tropism of AAV through pseudotyping, or the mixing of a capsid and genome from different viral serotypes. These serotypes are denoted using a slash, so that AAV2/5 indicates a virus containing the genome of serotype 2 packaged in the capsid from serotype 5. Use of these pseudotyped viruses can improve transduction efficiency, as well as alter tropism. For example, AAV2/5 targets neurons that are not efficiently transduced by AAV2/2, and is distributed more widely in the brain, indicating improved transduction efficiency. Many of these hybrid viruses have been well characterized and may be preferred over standard viruses for in vivo applications.
AAV plasmids
Helper Plasmid
pAdDeltaF6: Helper plasmid for AAV packaging, expressing adenovirus E4, E2A and VA for all serotypes
RepCap Plasmids
pAAV2/1: AAV packaging plasmid, expressing Rep2 and Cap1
pAAV2/2: AAV packaging plasmid, expressing Rep2 and Cap2
pAAV2/5: AAV packaging plasmid, expressing Rep2 and Cap5
pAAV2/7: AAV packaging plasmid, expressing Rep2 and Cap7
pAAV2/8: AAV packaging plasmid, expressing Rep2 and Cap8
pAAV2/9n: AAV packaging plasmid, expressing Rep2 and Cap9
pAAV2/rh10: AAV packaging plasmid, expressing Rep2, and rh10 capsid
pAAV2-7M8: AAV packaging plasmid, expressing Rep2 and 7M8 capsid
Souce: NovoPro 2023-08-18
