-
Product Name
Human SIRPA/BIT/MFR/MYD1/PTPNS1 (Fc tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Signal Regulatory Protein α (SIRPα) is a monomeric approximately 90 kD type I transmembrane glycoprotein. The 504 amino acid human SIRPα contains two Ig-like C1-type domains and one Ig-like V-type domain. SIRPα can express in various tissues, mainly on brain and myeloid cells, including macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic and Langerhans cells. It also can detect in neurons, smooth muscle and endothelial cells. SIRPA is an immunoglobulin-like cell surface receptor for CD47. SIRPα acts as docking protein and induces translocation of PTPN6, PTPN11 and other binding partners from the cytosol to the plasma membrane. SIRPα shows adhesion of cerebellar neurons, neurite outgrowth and glial cell attachment. SIRPα engagement generally produces a negative regulatory signal; it may mediate negative regulation of phagocytosis, mast cell activation and dendritic cell activation
-
Protein name
signal regulatory protein alpha(SIRPA)
-
Protein short names
BIT; MFR; MYD1; PTPNS1; SHPS1; SIRP
-
Uniprot ID
P78324
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the Human SIRPA/BIT/MFR/MYD1/PTPNS1 Glu31-Arg370 is expressed with a Fc tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Human
-
Purity
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
Validations
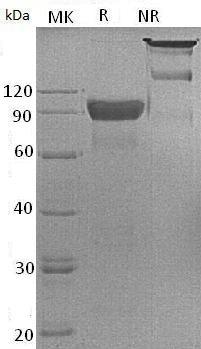
Human SIRPA/BIT/MFR/MYD1/PTPNS1 (Fc tag) recombinant protein
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
