-
Product Name
GMF-beta antibody
- Documents
-
Description
GMF-beta Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human colon cancer tissue. Positive WB detected in rat brain tissue, human brain tissue, human heart tissue, mouse brain tissue, mouse heart tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 17 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, IHC, WB
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
Glia maturation factor beta antibody; glia maturation factor antibody; beta antibody; GMF antibody; GMF beta antibody; GMFB antibody; GMF-β antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of GMF-beta recombinant protein (Accession Number: BC005359). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
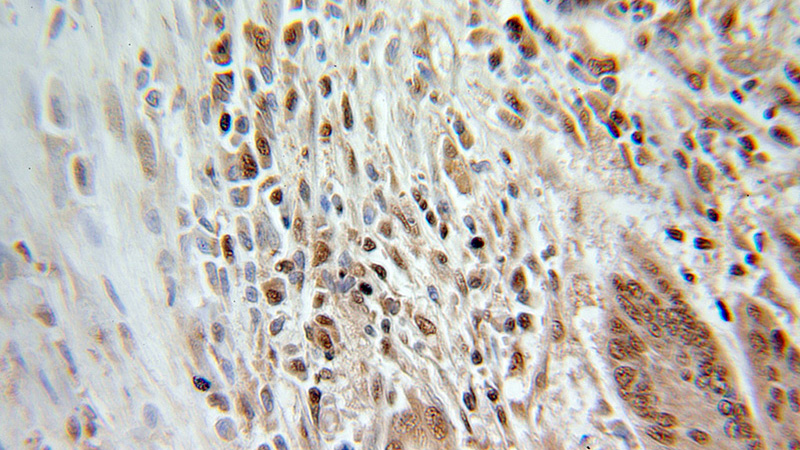
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human colon cancer using Catalog No:111098(GMFB antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 25x lens)
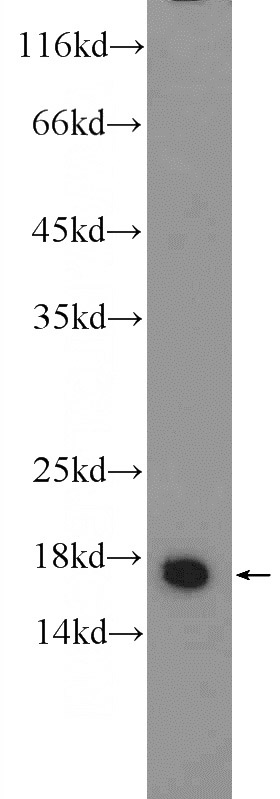
rat brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:111098(GMFB Antibody) at dilution of 1:500
-
Background
GMFB, Glia maturation factor beta, is a nerve growth factor implicated in nervous system development. It was reported that GMF-beta promotes the phenotypic expression of glia and neurons and inhibits the proliferation of their respective tumors in culture cells. GMF-beta protein is specific to the brain where it is expressed in glial cells (mainly astrocytes) and insome neurons. Higher levels of GMFB were found in the central nervous system, except for the spinal cord, and in thymus and colon.
-
References
- Li YL, Ye F, Cheng XD. Identification of glia maturation factor beta as an independent prognostic predictor for serous ovarian cancer. European journal of cancer (Oxford, England : 1990). 46(11):2104-18. 2010.
- Nam J, Onitsuka I, Hatch J. Coronary veins determine the pattern of sympathetic innervation in the developing heart. Development (Cambridge, England). 140(7):1475-85. 2013.
- Kempuraj D, Thangavel R, Yang E. Dopaminergic Toxin 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium, Proteins α-Synuclein and Glia Maturation Factor Activate Mast Cells and Release Inflammatory Mediators. PloS one. 10(8):e0135776. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
