-
Product Name
Canine CTLA-4/CD152 (His Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4, also known as CTLA4 and CD152, is a single-pass type I membrane protein and a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is the second member of the CD28 receptor family. The ligands or counterreceptors for these two proteins are the B7 family members, CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2). CTLA4 transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells, whereas CD28 transmits a stimulatory signal. Intracellular CTLA4 is also found in regulatory T cells and may play an important role in their functions. CD152 or cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) is an essential receptor involved in the negative regulation of T cell activation. Because of its profound inhibitory role, CD152 has been considered a sound susceptible candidate in autoimmunity and a persuasive target for cancer immunotherapy. In particular, recent evidence suggests that CD152 is also important in the homeostasis and function of a population of suppressive cells, termed regulatory T cells (Treg).
-
Protein name
Costimulatory molecule B7 receptor CD152
-
Protein short names
CELIAC3; GRD4; CTLA-4; CD152; IDDM12; GSE; ICOS; ALPS5; CH29-120A16.2; LY-56; CTLA4; CD
-
Uniprot ID
Q9GKP2
-
Gene Name
CD152; CTLA4
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the canine CD152 (NP_001003106.1) (Met1-Asp161) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Canine
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant canine CD152 consists 137 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 14.8 kDa.
-
Purity
> 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
Validations
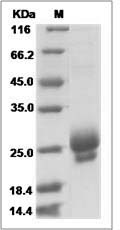
CTLA4 protein SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
