-
Product Name
NF-κB antibody
- Documents
-
Description
NF-κB Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in Jurkat cells, HeLa cells, K-562 cells, Raji cells. Positive IP detected in Jurkat cells. Positive IF detected in HeLa cells. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 50 kDa and 105 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IF, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human, Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
DKFZp686C01211 antibody; DNA binding factor KBF1 antibody; EBP 1 antibody; KBF1 antibody; NF kappa B antibody; NFKB p105 antibody; NFKB p50 antibody; NFKB1 antibody; NFKB1 antibody; p105 antibody; NFKB1 antibody; p105 antibody; p50 antibody; NF-κB antibody; p105 antibody; p50 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of NF-κB recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_003998). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IF: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations

Jurkat cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:113169(NFKB1 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
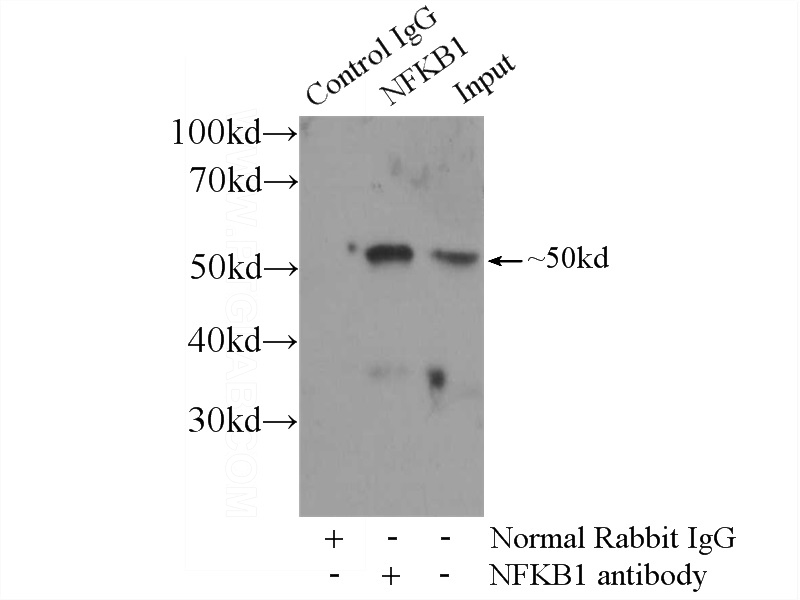
IP Result of anti-NFKB1 (IP:Catalog No:113169, 3ug; Detection:Catalog No:113169 1:500) with Jurkat cells lysate 1800ug.
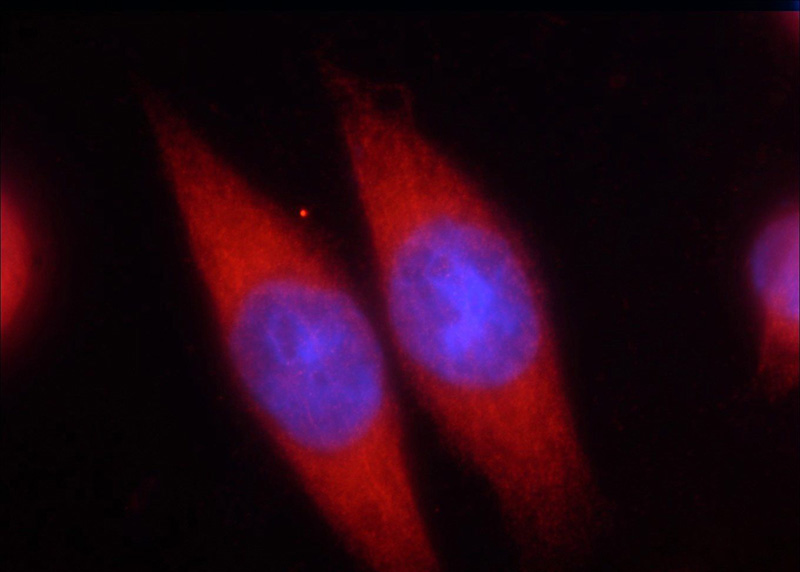
Immunofluorescent analysis of HeLa cells using Catalog No:113169(NFKB1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 and Rhodamine-Goat anti-Rabbit IgG
-
Background
NFkB is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NFkB is activated by various intra- and extracellular stimuli such as cytokines, oxidant free radicals, ultraviolet irradiation, and bacterial or viral products. NFkB is a family of transcription factors that consists of homo- and heterodimers of NFkB1/p50 and RelA/p65 subunits, and controls a variety of cellular events including development and immune responses. All members share a conserved amino terminus domain that includes dimerization, nuclear localization, and DNA binding regions, and a carboxy terminal transactivation domain. Serines 529 and 536 in the transactivation domain of RelA/p65 are phosphorylated in response to several stimuli including phorbol ester, IL1 alpha and TNF alpha as mediated by IkB kinase and p38 MAPK. Phosphorylation of serines 529 and 536 is critical for RelA/p65 transcriptional activity. Activated NFkB translocates into the nucleus and stimulates the expression of genes involved in a wide variety of biological functions. Inappropriate activation of NFkB has been associated with a number of inflammatory diseases while persistent inhibition of NFkB leads to inappropriate immune cell development or delayed cell growth. NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing. This antibody can bind both p105 and p50 isoforms of NFKB1.
-
References
- Zhang J, Wang S, Wang K, Zheng C. Herpes simplex virus 1 DNA polymerase processivity factor UL42 inhibits TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation by interacting with p65/RelA and p50/NF-κB1. Medical microbiology and immunology. 202(4):313-25. 2013.
- Luo J, Zhou H, Wang F. The hepatitis B virus X protein downregulates NF-κB signaling pathways through decreasing the Notch signaling pathway in HBx-transformed L02 cells. International journal of oncology. 42(5):1636-43. 2013.
- Zhang J, Wang K, Wang S, Zheng C. Herpes simplex virus 1 E3 ubiquitin ligase ICP0 protein inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced NF-κB activation by interacting with p65/RelA and p50/NF-κB1. Journal of virology. 87(23):12935-48. 2013.
- Liu M, Xu Y, Han X. Potent effects of flavonoid-rich extract from Rosa laevigata Michx fruit against hydrogen peroxide-induced damage in PC12 cells via attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). 19(8):11816-32. 2014.
- Mao Q, Xie Z, Wang X. Clonorchis sinensis ferritin heavy chain triggers free radicals and mediates inflammation signaling in human hepatic stellate cells. Parasitology research. 114(2):659-70. 2015.
- Zhai Y, Wu B, Li J, Yao XY, Zhu P, Chen ZN. CD147 promotes IKK/IκB/NF-κB pathway to resist TNF-induced apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Journal of molecular medicine (Berlin, Germany). 94(1):71-82. 2016.
- Mao Y, Zhang S, Yu F, Li H, Guo C, Fan X. Ghrelin Attenuates Liver Fibrosis through Regulation of TGF-β1 Expression and Autophagy. International journal of molecular sciences. 16(9):21911-30. 2015.
- Zhang F, Zhang Y, Wang K. Diallyl trisulfide inhibits naphthalene-induced oxidative injury and the production of inflammatory responses in A549 cells and mice. International immunopharmacology. 29(2):326-33. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
