-
Product Name
Anti-NFkB p105/p50 (5E3) Mouse antibody
- Documents
-
Description
NFkB p105/p50 (5E3) Mouse monoclonal antibody
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
DKFZp686C01211; DNA binding factor KBF1; DNA binding factor KBF1 EBP1; DNA-binding factor KBF1; EBP 1; EBP-1; EBP1; KBF1; MGC54151; NF kappa B; NF kappaB; NF kappabeta; NF kB1; NFkappaB; NFKB 1; NFKB p105; NFKB p50; Nfkb1; NFKB1_HUMAN; Nuclear factor kapp antibody
-
Isotype
Mouse IgG1
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant human NF-κB1 p105/p50 protein.
-
Clonality
Monoclonal
-
Formulation
PBS(pH 7.4) containing with 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% glycerol.
-
Storage instructions
Store at 4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
-
Applications
WB: 1/500
-
Validations
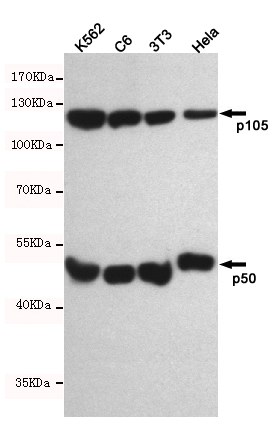
Western blot detection of NF-u03baB1 p105/p50 in K562, C6, 3T3 and Hela cell lysates using NF-u03baB1 p105/p50 mouse mAb(dilution 1:500).Predicted band size:120, 50kDa.Observed band size:120, 50kDa.
-
Background
Swiss-Prot Acc.P19838.NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity,differentiation,cell growth,tumorigenesis and apoptosis.NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65,RELB,NFKB1/p105,NFKB1/p50,REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one.The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity.Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors,respectively.NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors.NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family.In a conventional activation pathway,I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators,subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus.NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and RelB-p50 complexes are transcriptional activators.The NF-kappa-B p50-p50 homodimer is a transcriptional repressor,but can act as a transcriptional activator when associated with BCL3.NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing.The proteasome-mediated process ensures the production of both p50 and p105 and preserves their independent function,although processing of NFKB1/p105 also appears to occur post-translationally.p50 binds to the kappa-B consensus sequence 5'-GGRNNYYCC-3',located in the enhancer region of genes involved in immune response and acute phase reactions.In a complex with MAP3K8, NFKB1/p105 represses MAP3K8-induced MAPK signaling;active MAP3K8 is released by proteasome-dependent degradation of NFKB1/p105.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
