-
Product Name
Mouse CD14 (His Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
The cluster of differentiation (CD) system is commonly used as cell markers in immunophynotyping. Different kinds of cells in the immune system can be identified through the surface CD molecules which associating with the immune function of the cell. There are more than 320 CD unique clusters and subclusters have been identified. Some of the CD molecules serve as receptors or ligands important to the cell through initiating a signal cascade which then alter the behavior of the cell. Some CD proteins do not take part in cell signal process but have other functions such as cell adhesion. Cluster of differentiation 14 (CD14) is a member of the CD system. It takes its name from its inclusion in the CD molecule surface marker proteins. CD14 exists in two forms: a form anchored into the membrane or a soluble form. CD14 was found expressed in macrophages, neutrophil granulocyte and dendritic cells. The major function is serve as a co-receptor (along with TLR4 and MD-2) for the bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and other pathogen-associated molecular patterns.
-
Protein name
Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14
-
Protein short names
MONOCYTE DIFFERENTIATION ANTIGEN CD14; CD14 ANTIGEN; CD14
-
Uniprot ID
Q4FJP7
-
Gene Name
Cd14
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Pro 345) of mouse CD14 (NP_033971.1) precursor was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Mouse
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant mouse CD14 consists of 341 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 36.8 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rmCD14 is approximately 45-50 kDa due to glycosylation.
-
Purity
> 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Validations
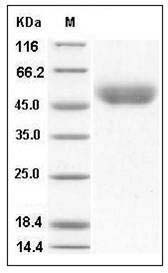
Mouse CD14 Protein (His Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
