-
Product Name
Human Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase / IVD (aa 30-423, His Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase, also known as IVD, plays an essential role in processing proteins obtained from the diet. The body breaks down proteins from food into smaller parts called amino acids. Amino acids can be further processed to provide energy for growth and development. Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase helps process a particular amino acid called leucine. Specifically, isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase is responsible for the third step in the breakdown of leucine. This step is a chemical reaction that converts a molecule called isovaleryl-CoA to another molecule, 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA. Additional chemical reactions convert 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA into molecules that are used for energy.
-
Protein name
Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial
-
Protein short names
ISOVALERYL COA DEHYDROGENASE; RP23-172B16.1; 6720455E18RIK; ISOVALERYL COENZYME A DEHYDROGENASE; ISOVALERYL DEHYDROGENASE; 1300016K07RIK; ACAD2; AI463340; ISOVALERYL-COA DEHYDROGENASE; MITOCHONDRIAL; IVD
-
Uniprot ID
P26440
-
Gene Name
IVD
-
Source/Expression Host
Baculovirus-Insect Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the human IVD (AAH17202.1) (His30-His423) was fused with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Human
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant human IVD consists of 412 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 45.3 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 43 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions.
-
Purity
> 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Validations
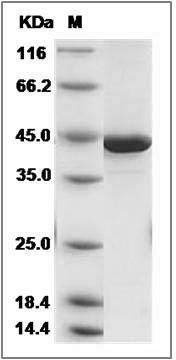
Human Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase / IVD Protein (aa 30-423, His Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
