-
Product Name
Human F9 (His tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Coagulation factor IX(F9), is a member of the peptidase S1 family. It contains two EGF-like domains, a Gla domain and a peptidase S1 domain. It is primarily expressed in the liver and secreted in plasma. Factor IX is a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein that participates in the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation by converting factor X to its active form in the presence of Ca2+ ions, phospholipids, and factor VIIIa. Mutations in position 43 and 46 prevents cleavage of the propeptide, mutation in position 93 probably fails to bind to cell membranes, mutation in position 191 or in position 226 prevent cleavage of the activation peptide. Mutations of human F9 can result in thrombophilia and recessive X-linked hemophilia B (HEMB). An X-linked blood coagulation disorder characterized by a permanent tendency to hemorrhage, due to factor IX deficiency. It is phenotypically similar to hemophilia A, but patients present with fewer symptoms. Many patients are asymptomatic until the hemostatic system is stressed by surgery or trauma.
-
Protein name
coagulation factor IX(F9)
-
Uniprot ID
P00740
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the Human F9 Thr29-Thr461 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Human
-
Purity
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
Validations
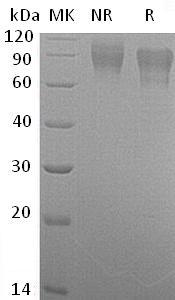
Human F9 (His tag) recombinant protein
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
