-
Product Name
Human EPO (His tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a glycoprotein hormone that is principally known for its role in erythropoiesis, where it is responsible for stimulating proliferation and differentiation of erythroid progenitor cells. Erythropoietin is a member of the EPO/TPO family. It is a secreted, glycosylated cytokine composed of four alpha helical bundles. The differentiation of CFU-E (Colony Forming Unit-Erythroid) cells into erythrocytes can only be accomplished in the presence of EPO. Physiological levels of EPO in adult mammals are maintained primarily by the kidneys, whereas levels in fetal or neonatal mammals are maintained by the liver. EPO also can exert various non-hematopoietic activities, including vascularization and proliferation of smooth muscle, neural protection during hypoxia, and stimulation of certain B cells. Genetic variation in erythropoietin is associated with susceptbility to microvascular complications of diabetes type 2. These are pathological conditions that develop in numerous tissues and organs as a consequence of diabetes mellitus. They include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy leading to end-stage renal disease, and diabetic neuropathy.
-
Protein name
erythropoietin(EPO)
-
Uniprot ID
P01588
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the Human EPO Ala28-Arg193 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Human
-
Purity
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
Validations
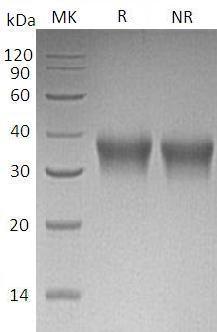
Human EPO (His tag) recombinant protein
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
