-
Product Name
EGLN1/EGLN2 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to EGLN1/EGLN2
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: A synthetic peptide of human EGLN1/EGLN2
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:50 - 1:200 -
Validations
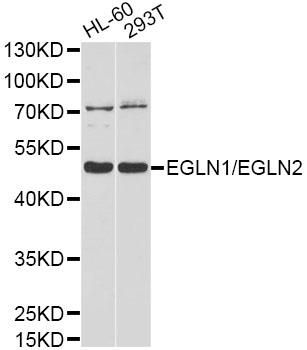
Western blot - EGLN1/EGLN2 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using EGLN1/EGLN2 antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 90s.
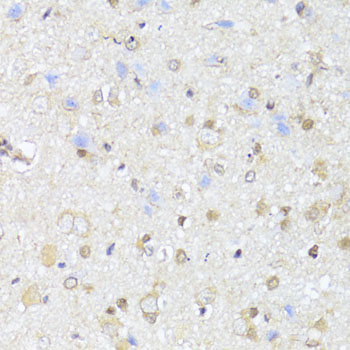
Immunohistochemistry - EGLN1/EGLN2 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat brain using EGLN1+EGLN2 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
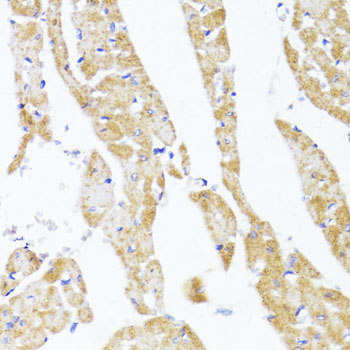
Immunohistochemistry - EGLN1/EGLN2 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat heart using EGLN1+EGLN2 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
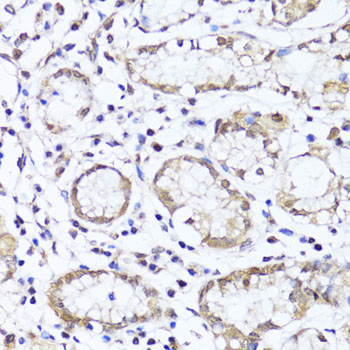
Immunohistochemistry - EGLN1/EGLN2 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human stomach using EGLN1+EGLN2 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
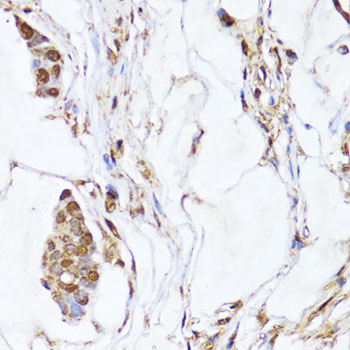
Immunohistochemistry - EGLN1/EGLN2 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human gastric cancer using EGLN1+EGLN2 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
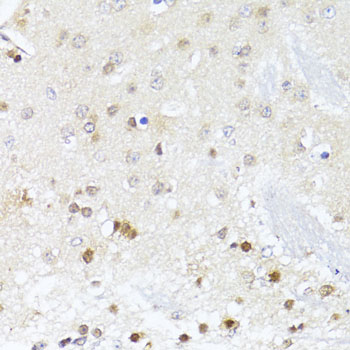
Immunohistochemistry - EGLN1/EGLN2 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse brain using EGLN1+EGLN2 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
-
Background
Cellular oxygen sensor that catalyzes, under normoxic conditions, the post-translational formation of 4-hydroxyproline in hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) alpha proteins. Hydroxylates a specific proline found in each of the oxygen-dependent degradation (ODD) domains (N-terminal, NODD, and C-terminal, CODD) of HIF1A. Also hydroxylates HIF2A. Has a preference for the CODD site for both HIF1A and HIF1B. Hydroxylated HIFs are then targeted for proteasomal degradation via the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitination complex. Under hypoxic conditions, the hydroxylation reaction is attenuated allowing HIFs to escape degradation resulting in their translocation to the nucleus, heterodimerization with HIF1B, and increased expression of hypoxy-inducible genes. EGLN1 is the most important isozyme under normoxia and, through regulating the stability of HIF1, involved in various hypoxia-influenced processes such as angiogenesis in retinal and cardiac functionality. Target proteins are preferentially recognized via a LXXLAP motif.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
