-
Product Name
APPL1 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
APPL1 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IP detected in mouse brain tissue. Positive WB detected in human brain tissue, HEK-293 cells, HeLa cells, HT-1080 cells, human heart tissue, mouse brain tissue. Positive IF detected in HepG2 cells. Positive IHC detected in human breast cancer tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 80 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IF, IHC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
APPL antibody; APPL1 antibody; Dip13 alpha antibody; DIP13A antibody; DIP13alpha antibody; KIAA1428 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of APPL1 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_012096). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:1000-1:10000
IP: 1:500-1:5000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
IF: 1:10-1:100
-
Validations
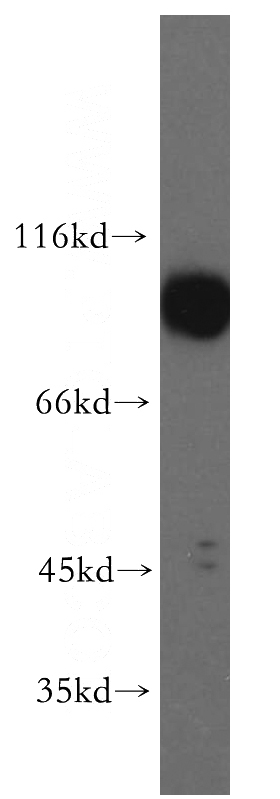
human brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:108041(APPL1 antibody) at dilution of 1:500
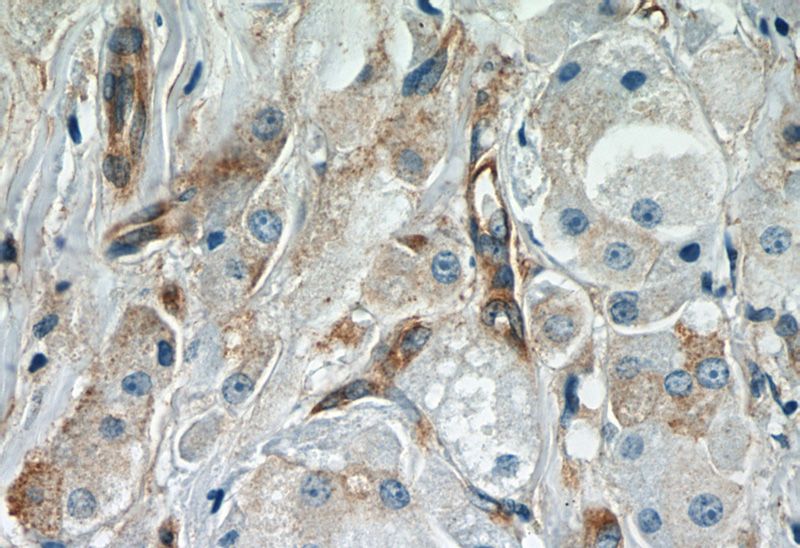
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer slide using Catalog No:108041(APPL1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:50
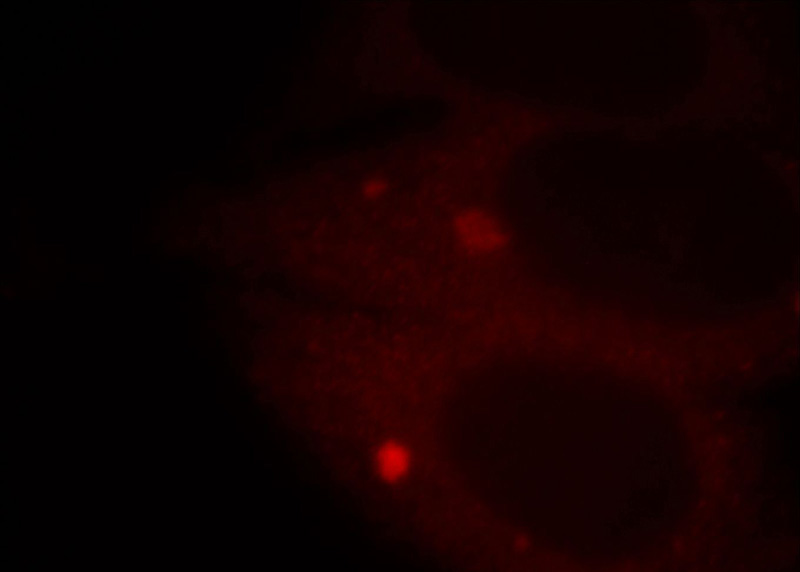
Immunofluorescent analysis of HepG2 cells, using APPL1 antibody Catalog No:108041 at 1:25 dilution and Rhodamine-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (red).
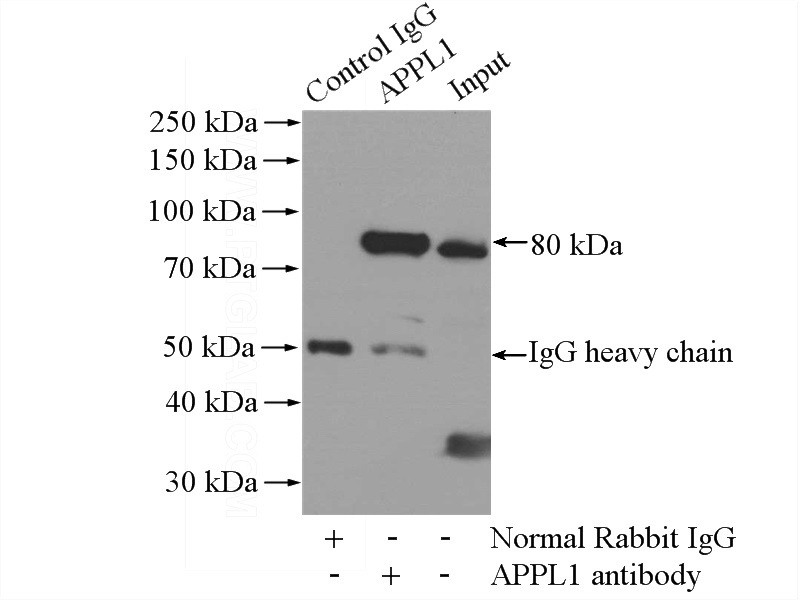
IP Result of anti-APPL1 (IP:Catalog No:108041, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:108041 1:1000) with mouse brain tissue lysate 2640ug.
-
Background
Adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interaction, PH domain and leucine zipper containing 1 (APPL1), a binding partner of Akt2 and an important regulator of insulin signaling, plays a key role in the regulation of insulin secretion [PMID:22615370]. APPL1 interacts with adiponectin receptors and mediates the insulin-sensitizing effects of adiponectin in muscle and endothelial cells. It also participates in nuclear signaling and transcriptional regulation, mostly by modulating the activity of various nuclear factors [PMID:22685329]. Apart from its role in endocytosis and endosomal transport, APPL1 was reported to undergo nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and participate in transcriptional regulation, e.g. by interactions with histone deacetylases (HDACs) [PMID:19686092].
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
