-
Product Name
Anti-Met antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Met
-
Tested applications
WB, ICC, IHC-P, FC
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
P antibody; HGF antibody; HGFR antibody; Par4 antibody; c-Met antibody; AI838057 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antigen of this antibody was synthetic peptide within mouse cmet aa 650-690.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
Liquid, 1*PBS (pH7.4), 0.2% BSA, 40% Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
-
Storage instructions
Store at +4℃ after thawing. Aliquot store at -20℃ or -80℃. Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB: 1:1,000
ICC: 1:200
IHC-P: 1:200
FC: 1:100-1:200
-
Validations
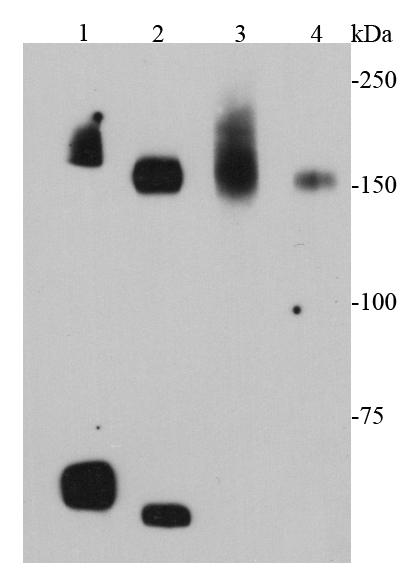
Fig1: Western blot analysis of cMet on different cell lysates using anti-cMet antibody at 1/1000 dilution.; Positive control:; Lane 1: Mouse liver; Lane 2: Mouse kidney; Lane 3: D3; Lane 4: MEF
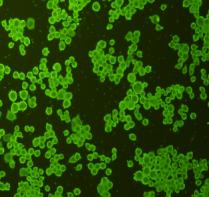
Fig2: ICC staining cMet in N2A cells (green). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
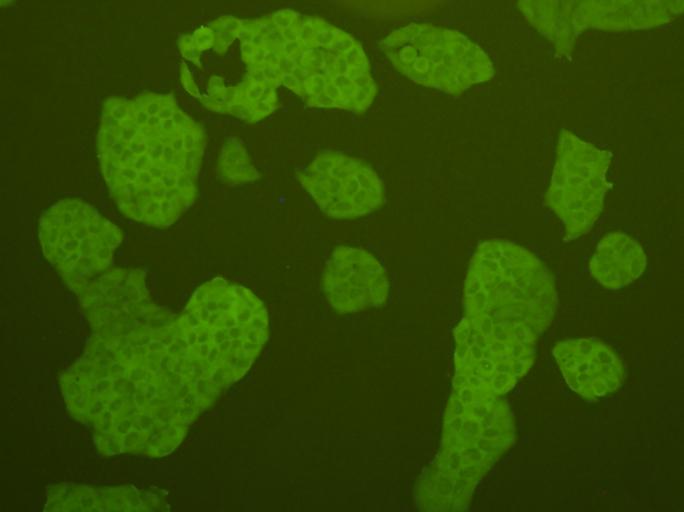
Fig3: ICC staining cMet in Hela cells (green). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
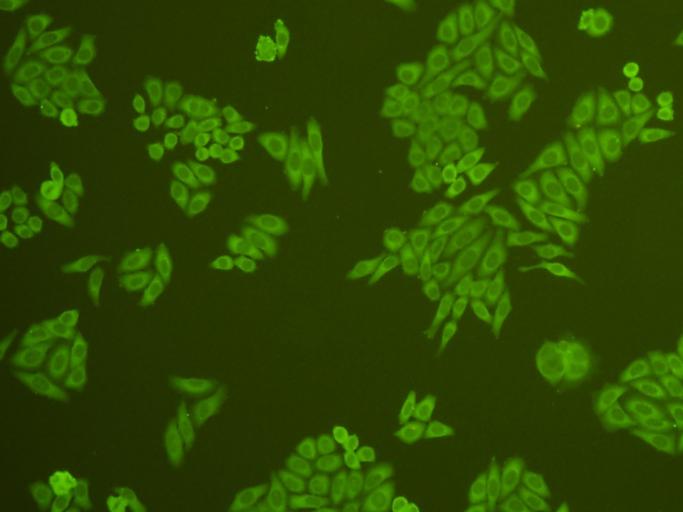
Fig4: ICC staining cMet in HepG2 cells (green). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
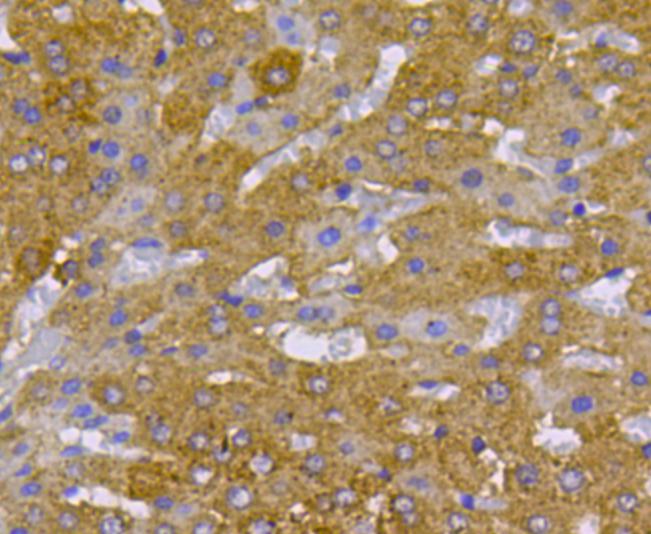
Fig5: Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse liver tissue using anti-cMet antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
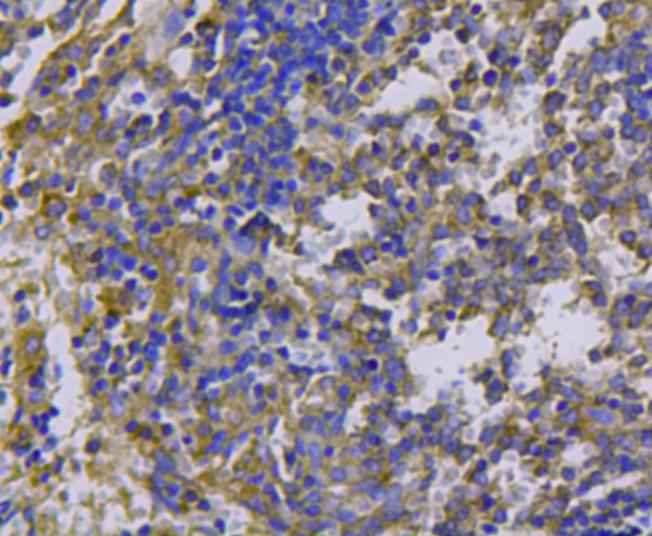
Fig6: Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse spleen tissue using anti-cMet antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
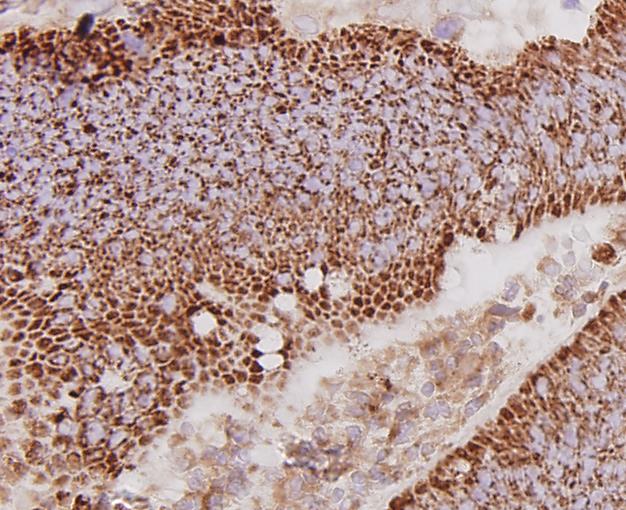
Fig7: Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human colon cancer tissue using anti-cMet antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
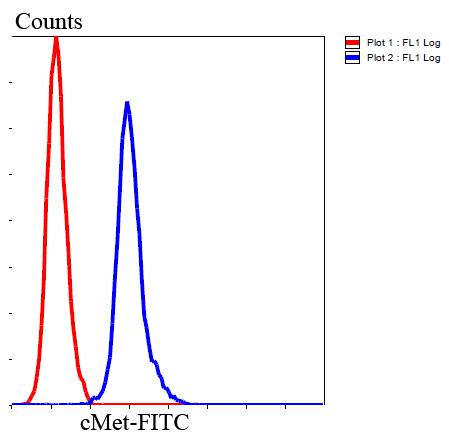
Fig8: Flow cytometric analysis of Hela cells with cMet antibody at 1/100 dilution (blue) compared with an unlabelled control (cells without incubation with primary antibody; red). Goat anti rabbit IgG (FITC) was used as the secondary antibody.
- Background
-
References
- Essential role for the c-met receptor in the migration of myogenic precursor cells into the limb bud. Bladt F., Riethmacher D., Isenmann S., Aguzzi A., Birchmeier C. Nature 376:768-771(1995)
- MUC20 suppresses the hepatocyte growth factor-induced Grb2-Ras pathway by binding to a multifunctional docking site of met. Higuchi T., Orita T., Katsuya K., Yamasaki Y., Akiyama K., Li H., Yamamoto T., Saito Y., Nakamura M. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24:7456-7468(2004)
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
