-
Product Name
Anti-Fer (9A10) Mouse antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Fer (9A10) Mouse monoclonal antibody
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse
-
Isotype
Mouse IgG1
-
Preparation
Antigen: Purified recombinant fragment of human FER expressed in E. Coli.
-
Clonality
Monoclonal
-
Formulation
Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide.
-
Storage instructions
Store at 4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
-
Applications
WB: 1/500 - 1/2000
IHC: 1/200 - 1/1000
ICC: 1/200 - 1/1000
ELISA: 1/10000
-
Validations
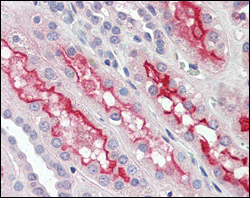
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human kidney tissues using FER mouse mAb.
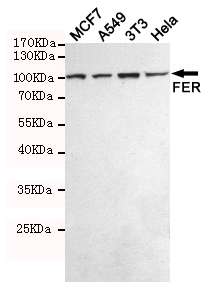
Western blot detection of FER in MCF7,A549,3T3 and Hela cell lysates using FER mouse mAb (1:500 diluted).Predicted band size:95KDa.Observed band size:95KDa.
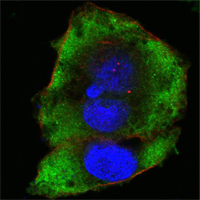
Confocal immunofluorescence analysis of Hela cells using FER mouse mAb (green). Red: Actin filaments have been labeled with Alexa Fluor-555 phalloidin. Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye.
-
Background
Swiss-Prot Acc.P16591.FER (fer tyrosine kinase) is a member of the FPS/FES family of nontransmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases, which shares a functional domain and is involved in signaling pathways through receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) and cytokine receptors. The Fes /Fps family is distinct from c-Src, c-Abl and related nRTKs and was originally distinguished as a homolog to retroviral oncoproteins. In vivo, Fer kinase assembles into homotrimers via conserved coiled-coil domains. The N-terminal coiled-coil domains of Fer can autophosphorylate in trans, thereby regulating their cellular function through differential phosphorylation states. Growth factor exposure can induce tyrosine phosphorylation of Fer and recruitment of Fer to RTK complexes containing p85. It is expressed predominantly in mature hematopoietic cells of the granulocytic and monocytic lineage, and has been shown to be expressed in vascular endothelial cells. Fer is implicated in insulin signaling, cell-cell signaling, human prostatic proliferative diseases, and is involved in the regulation of G1 progression.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
