-
Product Name
Anti-Argonaute-2 Rabbit antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Argonaute-2 Rabbit monoclonal antibody
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF, FC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
PPD; Q10; CASC7; EIF2C2; LINC00980 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: A synthetic peptide of human Argonaute-2
-
Clonality
Monoclonal
-
Formulation
50nM Tris-Glycine(pH 7.4), 0.15M Nacl, 40%Glycerol, 0.01% sodium azide and 0.05% BSA.
-
Storage instructions
Store at 4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
-
Applications
WB: 1/1000
IHC: 1/20
ICC/IF: 1/20-1/50
FC: 1/20
IP: 1/20
-
Validations
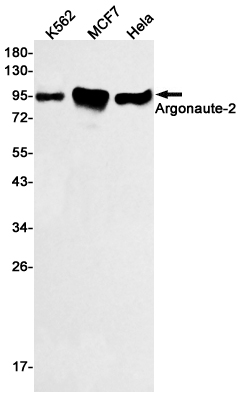
Western blot detection of Argonaute-2 in K562,MCF7,Hela cell lysates using Argonaute-2 Rabbit mAb(1:500 diluted).Predicted band size:97kDa.Observed band size:97kDa.
-
Background
Swiss-Prot Acc.Q9UKV8.Required for RNA-mediated gene silencing (RNAi) by the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The 'minimal RISC' appears to include AGO2 bound to a short guide RNA such as a microRNA (miRNA) or short interfering RNA (siRNA). These guide RNAs direct RISC to complementary mRNAs that are targets for RISC-mediated gene silencing. The precise mechanism of gene silencing depends on the degree of complementarity between the miRNA or siRNA and its target. Binding of RISC to a perfectly complementary mRNA generally results in silencing due to endonucleolytic cleavage of the mRNA specifically by AGO2. Binding of RISC to a partially complementary mRNA results in silencing through inhibition of translation, and this is independent of endonuclease activity. May inhibit translation initiation by binding to the 7-methylguanosine cap, thereby preventing the recruitment of the translation initiation factor eIF4-E. May also inhibit translation initiation via interaction with EIF6, which itself binds to the 60S ribosomal subunit and prevents its association with the 40S ribosomal subunit. The inhibition of translational initiation leads to the accumulation of the affected mRNA in cytoplasmic processing bodies (P-bodies), where mRNA degradation may subsequently occur. In some cases RISC-mediated translational repression is also observed for miRNAs that perfectly match the 3' untranslated region (3'-UTR). Can also up-regulate the translation of specific mRNAs under certain growth conditions. Binds to the AU element of the 3'-UTR of the TNF (TNF-alpha) mRNA and up-regulates translation under conditions of serum starvation. Also required for transcriptional gene silencing (TGS), in which short RNAs known as antigene RNAs or agRNAs direct the transcriptional repression of complementary promoter regions.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
