-
Product Name
RUNX1T1 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
RUNX1T1 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in HepG2 cells, Jurkat cells, mouse brain tissue. Positive IP detected in mouse brain tissue. Positive IHC detected in mouse brain tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 70-80 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
AML1T1 antibody; CBFA2T1 antibody; CDR antibody; Cyclin D related protein antibody; Eight twenty one protein antibody; ETO antibody; MTG8 antibody; MTG8b antibody; Protein CBFA2T1 antibody; Protein ETO antibody; Protein MTG8 antibody; RUNX1T1 antibody; ZMYND2 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of RUNX1T1 recombinant protein (Accession Number: XM_024447318). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:2000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
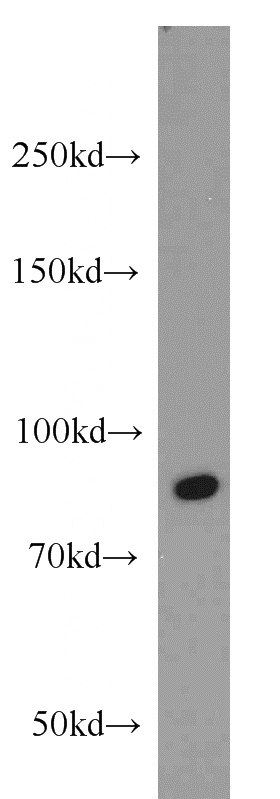
HepG2 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:114937(RUNX1T1 antibody) at dilution of 1:600
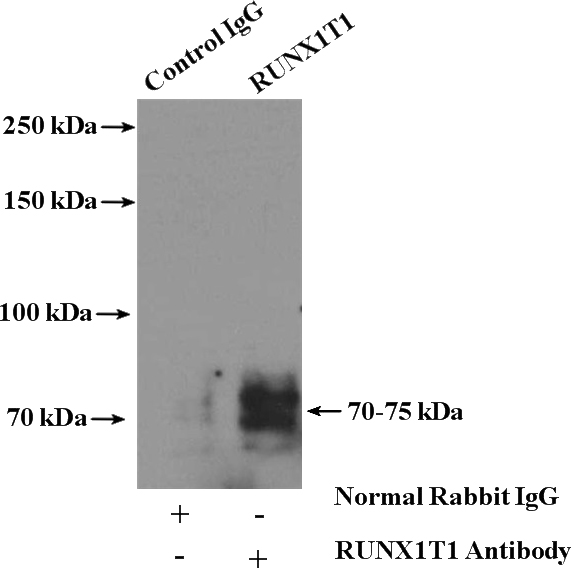
IP Result of anti-RUNX1T1 (IP:Catalog No:114937, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:114937 1:800) with mouse brain tissue lysate 3600ug.
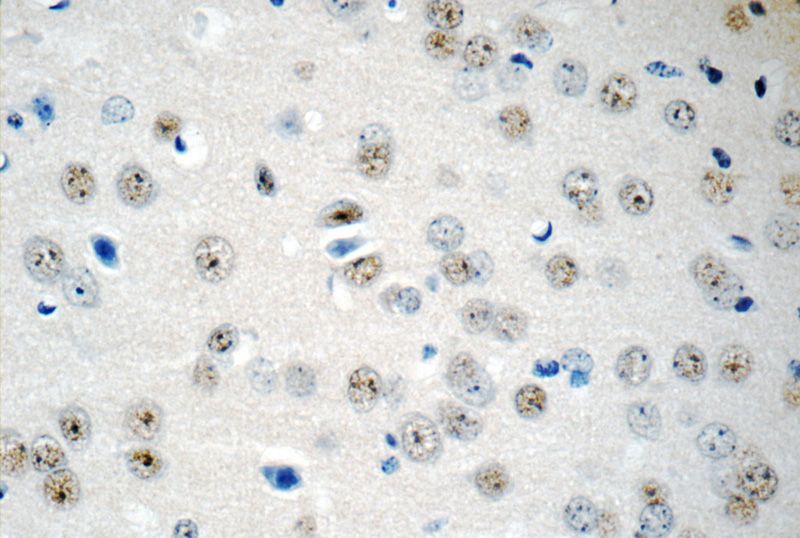
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue slide using Catalog No:114937(RUNX1T1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
-
Background
RUNX1T1 is a putative zinc finger transcription factor and oncoprotein. In acute myeloid leukemia, especially in the M2 subtype, the t(8;21)(q22;q22) translocation is one of the most frequent karyotypic abnormalities. The translocation produces a chimeric gene made up of the 5'-region of the RUNX1 gene fused to the 3'-region of this gene. Various transcript of the fusion gene has been reported.
-
References
- Zhao X, Yang Y, Sun BF. FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is required for adipogenesis. Cell research. 24(12):1403-19. 2014.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
