-
Product Name
ROGDI antibody
- Documents
-
Description
ROGDI Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human kidney tissue, human placenta tissue, human spleen tissue. Positive IP detected in mouse brain tissue. Positive WB detected in human brain tissue, human kidney tissue, mouse brain tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 32kd
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
FLJ22386 antibody; Protein rogdi homolog antibody; ROGDI antibody; rogdi homolog (Drosophila) antibody
- Immunogen
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of ROGDI recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_024589). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
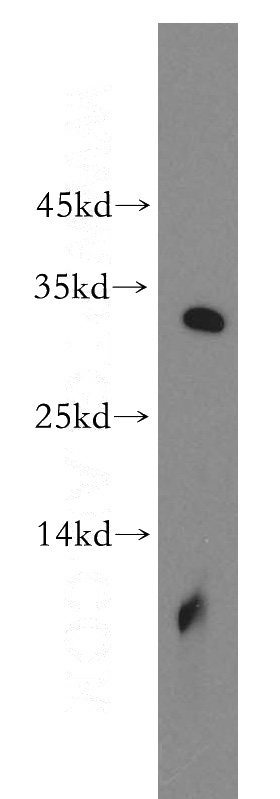
human brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:114782(ROGDI antibody) at dilution of 1:500
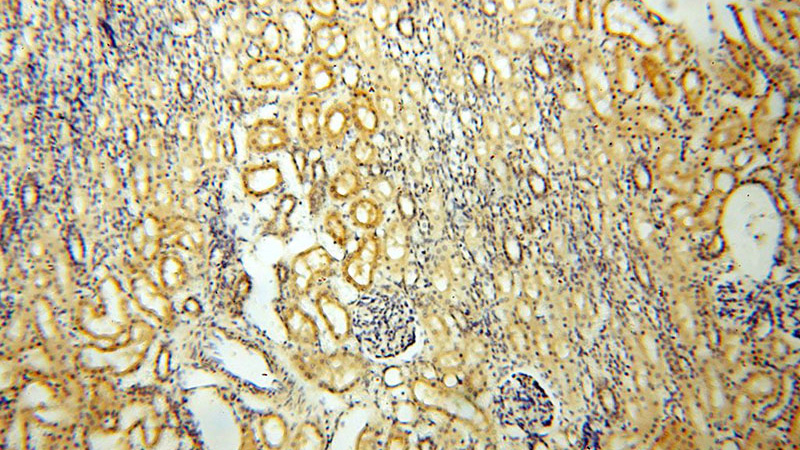
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human kidney using Catalog No:114782(ROGDI antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 10x lens)
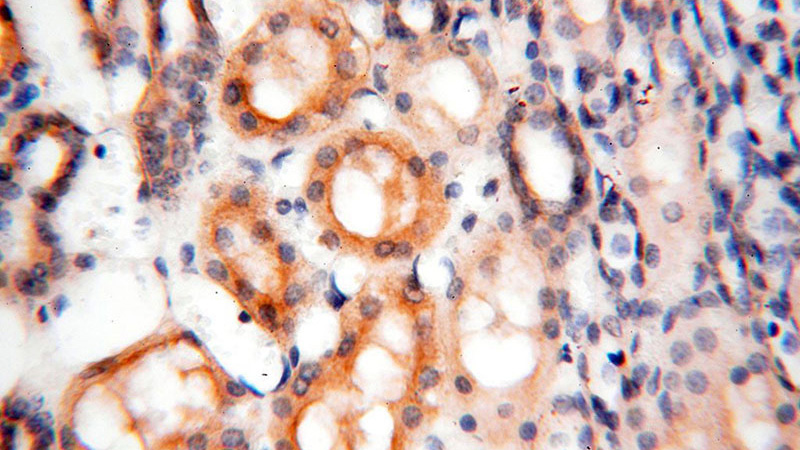
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human kidney using Catalog No:114782(ROGDI antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 40x lens)

IP Result of anti-ROGDI (IP:Catalog No:114782, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:114782 1:500) with mouse brain tissue lysate 4000ug.
-
Background
ROGDI encoded by the ROGDI gene, which encodes a leucine-zipper protein with high expression in the human spinal cord and brain, acts as a positive regulator of cell proliferation. Defections of ROGDI are the cause of Kohlschuetter-Toenz syndrome (KTZS)
-
References
- Schossig A, Wolf NI, Fischer C. Mutations in ROGDI Cause Kohlschütter-Tönz Syndrome. American journal of human genetics. 90(4):701-7. 2012.
- Mory A, Dagan E, Illi B. A nonsense mutation in the human homolog of Drosophila rogdi causes Kohlschutter-Tonz syndrome. American journal of human genetics. 90(4):708-14. 2012.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
