-
Product Name
REDD1 specific antibody
- Documents
-
Description
REDD1 specific Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human lung cancer tissue, human breast cancer tissue, human gliomas tissue, human heart tissue, human kidney tissue, human liver tissue, human pancreas cancer tissue, human placenta tissue, human spleen tissue, human testis tissue. Positive IP detected in MCF-7 cells. Positive WB detected in K-562 cells, A549 cells, DU 145 cells, LNCaP cells, MCF7 cells, PC-3 cells, Raji cells. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 35 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, IHC, IP, WB
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
DDIT4 antibody; Dig2 antibody; FLJ20500 antibody; REDD 1 antibody; REDD1 antibody; RP11 442H21.1 antibody; RTP801 antibody
- Immunogen
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of REDD1 specific recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_019058). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
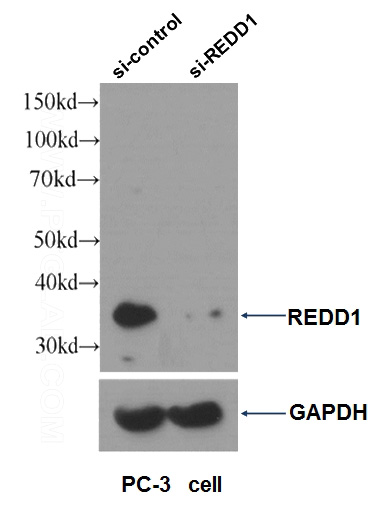
WB result of REDD1 antibody (Catalog No:114678, 1:1000) with si-control and si-REDD1 transfected PC-3 cells.

K-562 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:114678(REDD1 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000

IP Result of anti-REDD1 (IP:Catalog No:114678, 3ug; Detection:Catalog No:114678 1:500) with MCF-7 cells lysate 2500ug.
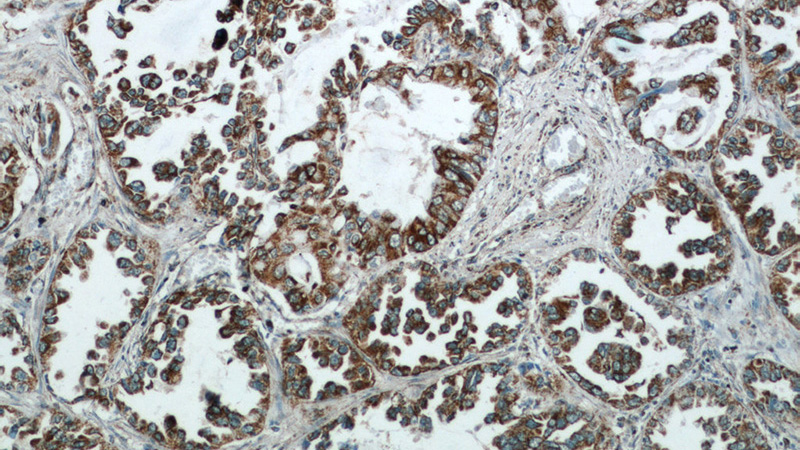
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer using Catalog No:114678(REDD1 antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)
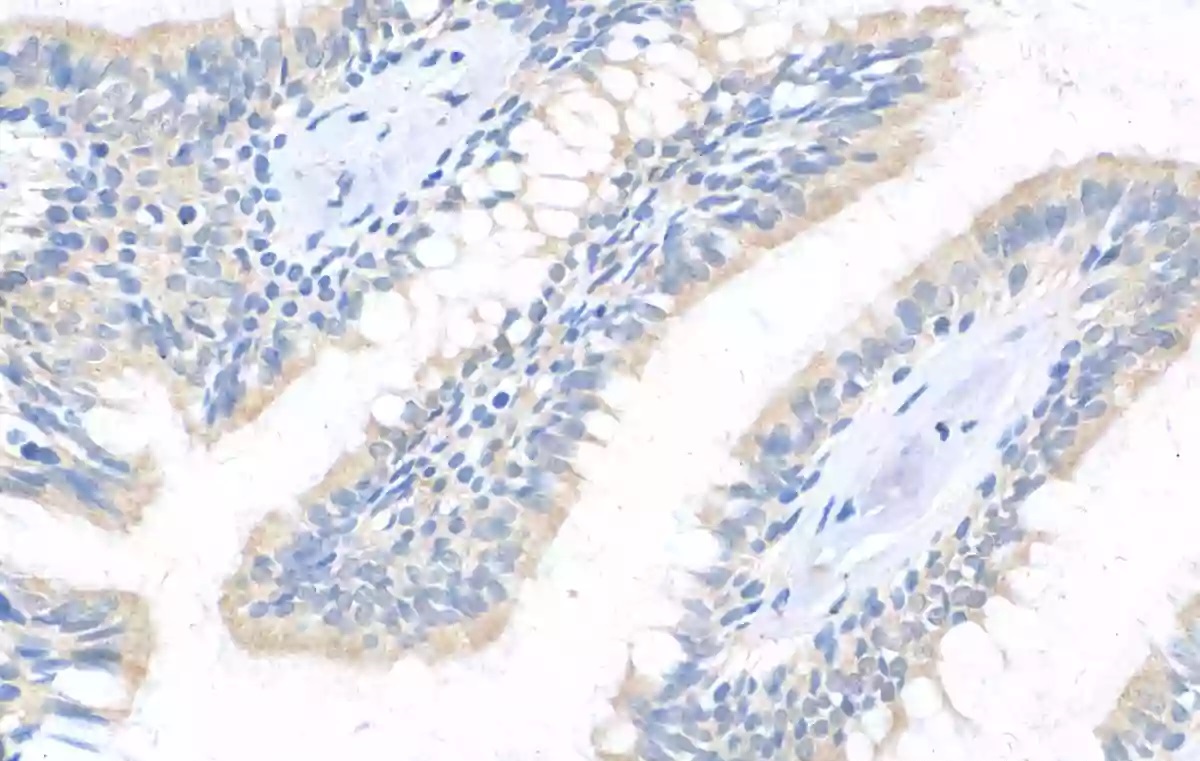
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer using Catalog No:114678(REDD1 antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
-
Background
REDD1, also named as RTP801 and DDIT4, belongs to the DDIT4 family. REDD1 promotes neuronal cell death. It is a novel transcriptional target of p53 implicated ROS in the p53-dependent DNA damage response. REDD1 controlled cell growth under energy stress, as an essential regulator of TOR activity through the TSC1/2 complex. REDD-1 expression has also been linked to apoptosis, Aβ toxicity and the pathogenesis of ischemic diseases. As an HIF-1-responsive gene, REDD-1 exhibits strong hypoxia-dependent upregulation in ischemic cells of neuronal origin[PMID: 19996311]. In response to stress due to DNA damage and glucocorticoid treatment, REDD-1 is upregulated at the transcriptional level[PMID: 21733849]. REDD-1 negatively regulates the mammalian target of Rapamycin, a serine/threonine kinase often referred to as mTOR[PMID: 22951983]. It is crucial in the coupling of extra- and intracellular cues to mTOR regulation. The absence of REDD-1 is associated with the development of retinopathy, a major cause of blindness[PMID: 22304497]. REDD1 is a new host defense factor, and chemical activation of REDD1 expression represents a potent antiviral intervention strategy[PMID: 21909097]. The calculated molecular weight of REDD1 is 25 kDa. Because of multiple lysines in the proteins, REDD1 offen migrates around 35 kDa on Western blot[PMID: 19221489]. This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against full length human REDD1 antigen. This antibody is specific ti the REDD1 from siRNA experiment (PMID:24713927)
-
References
- Schneider A, Younis RH, Gutkind JS. Hypoxia-induced energy stress inhibits the mTOR pathway by activating an AMPK/REDD1 signaling axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasia (New York, N.Y.). 10(11):1295-302. 2008.
- Lin CJ, Robert F, Sukarieh R, Michnick S, Pelletier J. The antidepressant sertraline inhibits translation initiation by curtailing mammalian target of rapamycin signaling. Cancer research. 70(8):3199-208. 2010.
- Liu C, Xue R, Wu D. REDD1 attenuates cardiac hypertrophy via enhancing autophagy. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 454(1):215-20. 2014.
- Baida G, Bhalla P, Kirsanov K. REDD1 functions at the crossroads between the therapeutic and adverse effects of topical glucocorticoids. EMBO molecular medicine. 7(1):42-58. 2015.
- Desantis A, Bruno T, Catena V. Che-1-induced inhibition of mTOR pathway enables stress-induced autophagy. The EMBO journal. 34(9):1214-30. 2015.
- Dungan CM, Wright DC, Williamson DL. Lack of REDD1 reduces whole body glucose and insulin tolerance, and impairs skeletal muscle insulin signaling. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 453(4):778-83. 2014.
- Dennis MD, Kimball SR, Fort PE, Jefferson LS. Regulated in development and DNA damage 1 is necessary for hyperglycemia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression in the retina of diabetic rodents. The Journal of biological chemistry. 290(6):3865-74. 2015.
- Gordon BS, Williamson DL, Lang CH, Jefferson LS, Kimball SR. Nutrient-induced stimulation of protein synthesis in mouse skeletal muscle is limited by the mTORC1 repressor REDD1. The Journal of nutrition. 145(4):708-13. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
