-
Product Name
PHYH antibody
- Documents
-
Description
PHYH Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in human liver tissue, HEK-293 cells, human kidney tissue, Jurkat cells. Positive IHC detected in human kidney tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 36 kDa, 70 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
LN1 antibody; LNAP1 antibody; PAHX antibody; PHYH antibody; PHYH1 antibody; Phytanic acid oxidase antibody; phytanoyl CoA 2 hydroxylase antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of PHYH recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_006214). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
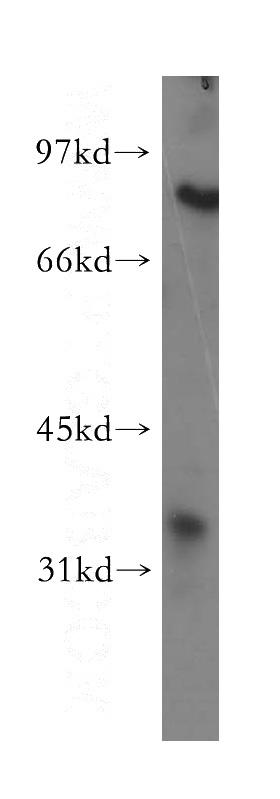
human liver tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:113864(PHYH antibody) at dilution of 1:500
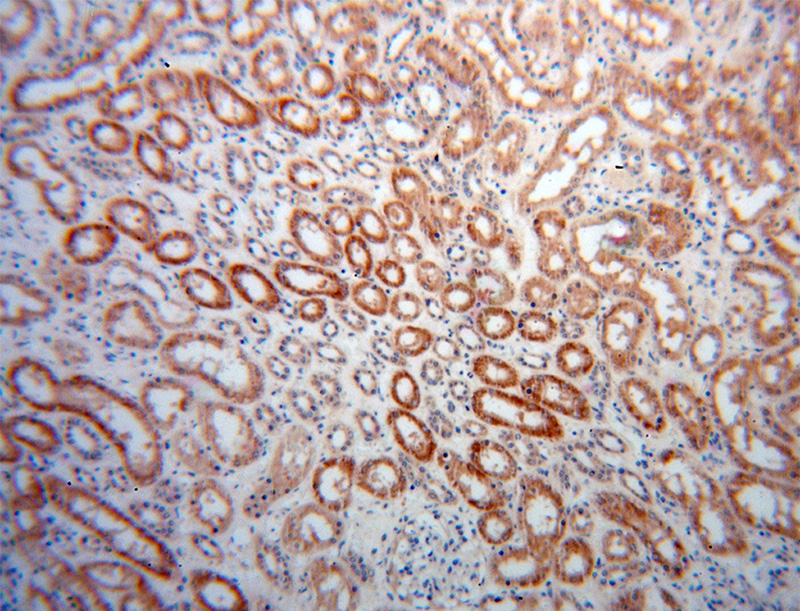
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human kidney using Catalog No:113864(PHYH antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)

Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human kidney using Catalog No:113864(PHYH antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
-
Background
PHYH (Phytanoyl-CoA 2-hydroxylase), also known as Phytanic acid oxidase or Phytanoyl-CoA alpha-hydroxylase, is a peroxisomal enzyme which converts phytanoyl-CoA to 2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA. It catalyzes the first step in the alpha-oxidation of phytanic acid, a branched-chain fatty acid. Mutations in this gene can cause Refsum disease (RD) and deficient protein activity can cause Zellweger syndrome and rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata. This antibody (12858-1-AP) detects two bands: 36kd and 70kd. The 70kd band may probably be the dimeric form of PHYH.
-
References
- Mizuno Y, Ninomiya Y, Nakachi Y. Tysnd1 deficiency in mice interferes with the peroxisomal localization of PTS2 enzymes, causing lipid metabolic abnormalities and male infertility. PLoS genetics. 9(2):e1003286. 2013.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
