-
Product Name
LRDD antibody
- Documents
-
Description
LRDD Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human pancreas tissue, human liver tissue. Positive IF detected in Hela cells. Positive IP detected in L02 cells. Positive WB detected in L02 cells, HEK-293 cells. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 55 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, IF, IP, WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
DKFZp434D229 antibody; LRDD antibody; PIDD antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of LRDD recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_145887). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:1000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
IF: 1:10-1:100
-
Validations
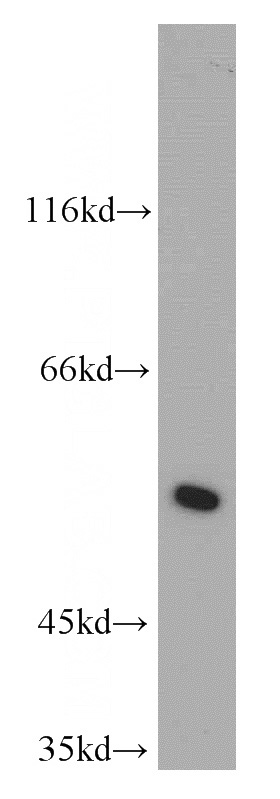
L02 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:112317(LRDD antibody) at dilution of 1:300

IP Result of anti-LRDD (IP:Catalog No:112317, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:112317 1:500) with L02 cells lysate 2800ug.
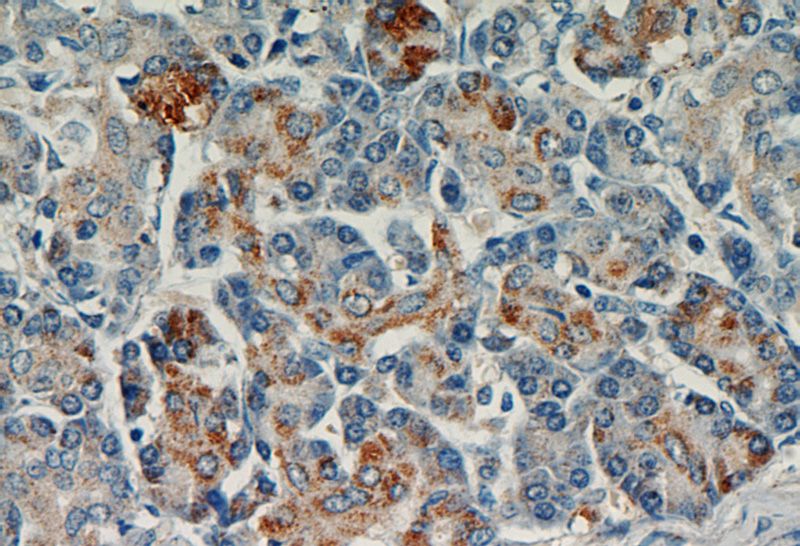
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human pancreas using Catalog No:112317(LRDD antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
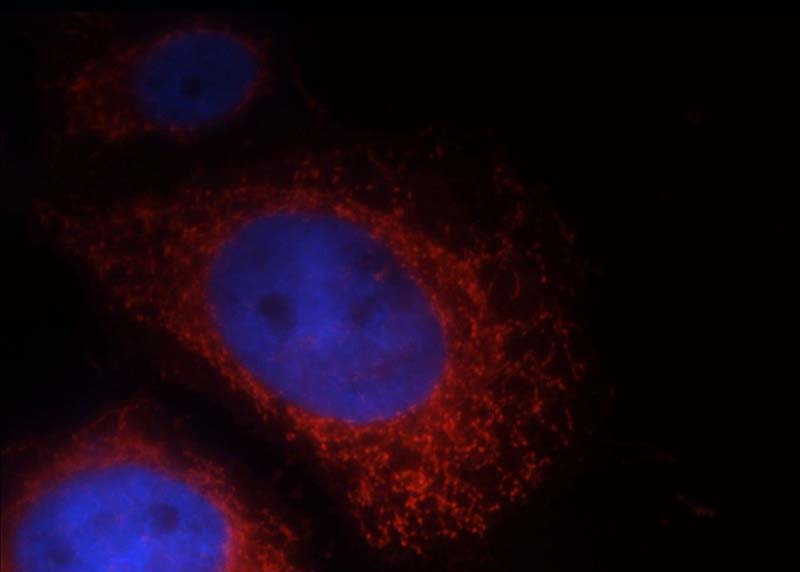
Immunofluorescent analysis of Hela cells, using LRDD antibody Catalog No:112317 at 1:25 dilution and Rhodamine-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (red). Blue pseudocolor = DAPI (fluorescent DNA dye).
-
Background
P53-induced protein with a death domain (PIDD/LRDD) is a component of the PIDDosome. PIDD contains 910 residues with 7 leucine rich repeats (LRRs), 2 ZU-5 domains and a C-terminal death domain (DD). PIDD can be cleaved into shorter fragments generating a PIDD-N fragment of 48 kD (residues 1-446), a PIDD-C fragment of 51 kD (residues 447-910) and a PIDD-CC fragment of 37 kD (residues 589-910). Auto-cleavage of PIDD determines the downstream signaling events. The PIDD-C fragment mediates activation of NFκB via the recruitment of RIP1 and NEMO, while PIDD-CC causes caspase-2 activation, which leads to apoptosis.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
