-
Product Name
KRIT1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to KRIT1
-
Tested applications
WB, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
KRIT1 antibody; CAM antibody; CCM1 antibody; KRIT1, ankyrin repeat containing antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 467-736 of human KRIT1 (NP_919438.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IF 1:50 - 1:100 -
Validations
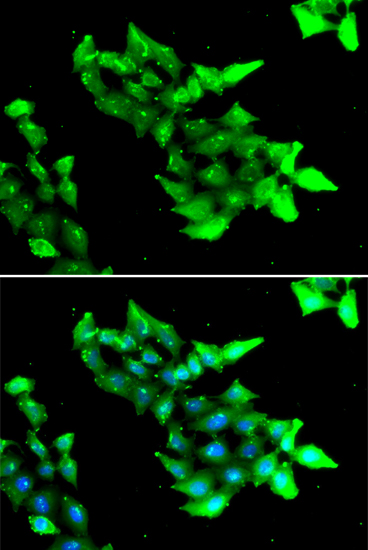
Immunofluorescence - KRIT1 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells using KRIT1 antibody . Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
-
Background
Component of the CCM signaling pathway which is a crucial regulator of heart and vessel formation and integrity (By similarity). Negative regulator of angiogenesis. Inhibits endothelial proliferation, apoptosis, migration, lumen formation and sprouting angiogenesis in primary endothelial cells. Promotes AKT phosphorylation in a NOTCH-dependent and independent manner, and inhibits ERK1/2 phosphorylation indirectly through activation of the DELTA-NOTCH cascade. Acts in concert with CDH5 to establish and maintain correct endothelial cell polarity and vascular lumen and these effects are mediated by recruitment and activation of the Par polarity complex and RAP1B. Required for the localization of phosphorylated PRKCZ, PARD3, TIAM1 and RAP1B to the cell junction, and cell junction stabilization. Plays a role in integrin signaling via its interaction with ITGB1BP1; this prevents the interaction between ITGB1 and ITGB1BP1. Microtubule-associated protein that binds to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2)-containing membranes in a GTP-bound RAP1-dependent manner. Plays an important role in the maintenance of the intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis to prevent oxidative cellular damage. Regulates the homeostasis of intracellular ROS through an antioxidant pathway involving FOXO1 and SOD2. Facilitates the down-regulation of cyclin-D1 (CCND1) levels required for cell transition from proliferative growth to quiescence by preventing the accumulation of intracellular ROS through the modulation of FOXO1 and SOD2 levels.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
