-
Product Name
ING5 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
ING5 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in Jurkat cells, HEK-293 cells, mouse kidney tissue, PC-3 cells. Positive IP detected in HEK-293 cells. Positive IHC detected in human colon cancer tissue, human ovary tumor tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 28-32 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
FLJ23842 antibody; ING5 antibody; Inhibitor of growth protein 5 antibody; p28ING5 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of ING5 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_001330162). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:2000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
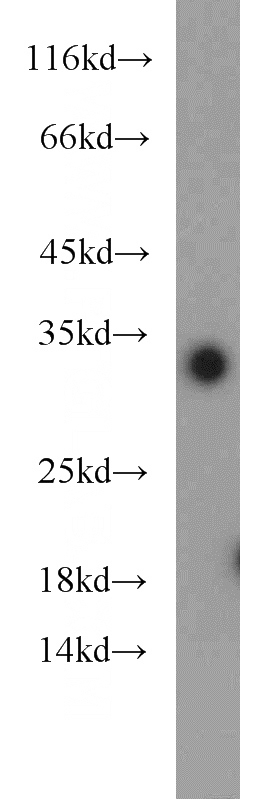
Jurkat cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:111797(ING5 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
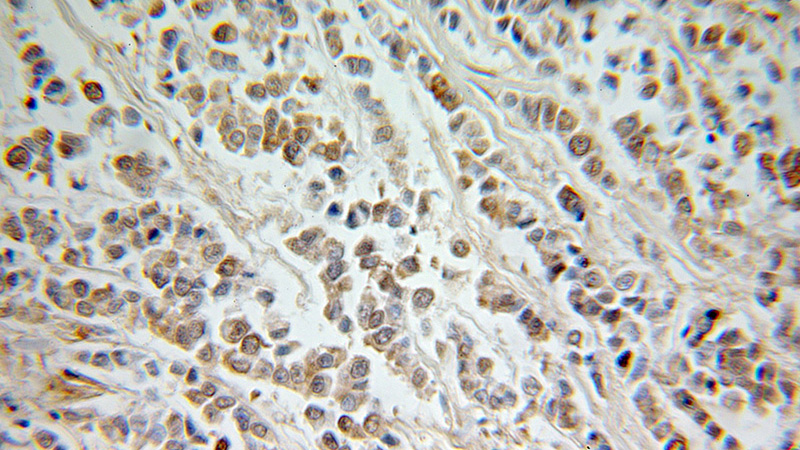
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human colon cancer using Catalog No:111797(ING5 antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 25x lens)
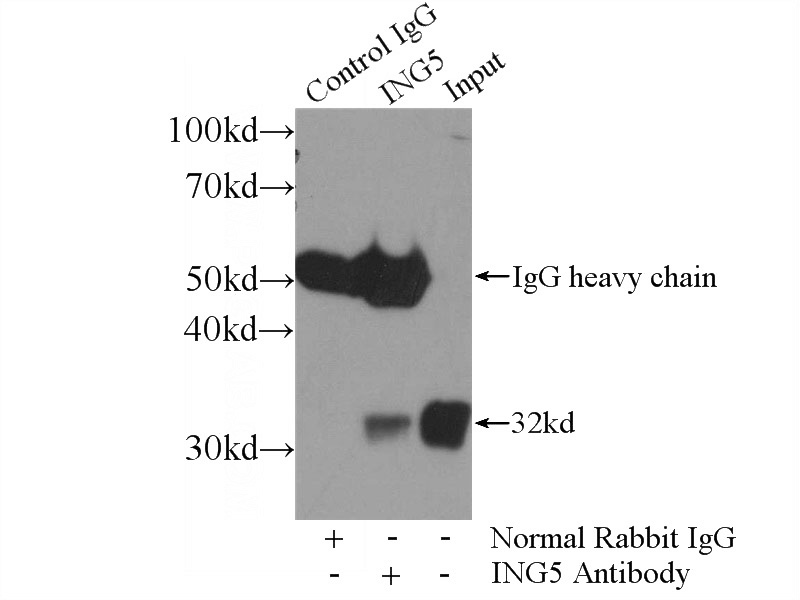
IP Result of anti-ING5 (IP:Catalog No:111797, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:111797 1:700) with HEK-293 cells lysate 2560ug.
-
Background
ING5, also named as p28ING5, belongs to the ING family. It is a component of the HBO1 complex which has a histone H4-specific acetyltransferase activity, a reduced activity toward histone H3 and is responsible for the bulk of histone H4 acetylation in vivo. ING5 is a component of the MOZ/MORF complex which has a histone H3 acetyltransferase activity. Through chromatin acetylation it may regulate DNA replication and may function as a transcriptional coactivator. (PMID:12750254) Altered ING5 expression and its shift into the cytoplasm may have an impact on the malignant transformation of colorectal epithelial cells and should be considered as a biomarker for colorectal carcinogenesis. (PMID:21193223)
-
References
- Wang J, Huang W, Wu Y. MicroRNA-193 pro-proliferation effects for bone mesenchymal stem cells after low-level laser irradiation treatment through inhibitor of growth family, member 5. Stem cells and development. 21(13):2508-19. 2012.
- Gou WF, Shen DF, Yang XF. ING5 suppresses proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion, and induces autophagy and differentiation of gastric cancer cells: a good marker for carcinogenesis and subsequent progression. Oncotarget. 6(23):19552-79. 2015.
- Cao Y, Chen J, Wang D. Upregulated in Hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma cells, miR-331-3p promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ING5. Oncotarget. 6(35):38093-106. 2015.
- Li X, Nishida T, Noguchi A. Decreased nuclear expression and increased cytoplasmic expression of ING5 may be linked to tumorigenesis and progression in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of cancer research and clinical oncology. 136(10):1573-83. 2010.
- Xing YN, Yang X, Xu XY. The altered expression of ING5 protein is involved in gastric carcinogenesis and subsequent progression. Human pathology. 42(1):25-35. 2011.
- Zheng HC, Xia P, Xu XY, Takahashi H, Takano Y. The nuclear to cytoplasmic shift of ING5 protein during colorectal carcinogenesis with their distinct links to pathologic behaviors of carcinomas. Human pathology. 42(3):424-33. 2011.
- Oh HS, Bryant KF, Nieland TJ. A targeted RNA interference screen reveals novel epigenetic factors that regulate herpesviral gene expression. mBio. 5(1):e01086-13. 2014.
- Lv L, Li Y, Deng H. MiR-193a-3p promotes the multi-chemoresistance of bladder cancer by targeting the HOXC9 gene. Cancer letters. 357(1):105-13. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
