-
Product Name
Human EphB4/Eph Receptor B4 (Fc Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Ephrin type-B receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPHB4 gene. It is a single-pass type I membrane protein belonging to the ephrin receptor subfamily of protein kinase superfamily. Members of the ephrin and Eph family are local mediators of cell function through largely contact-dependent processes in development and in maturity. Furthermore, EphB4 protein and the corresponding ligand Ephrin-B2 contribute to tumor growth in various human tumors. EphB4 protein has tumor suppressor activities and that regulation of cell proliferation, extracellular matrix remodeling, and invasive potential are important mechanisms of tumor suppression. Therefore, Ephrin-B2/EphB4 may be recognized as a novel prognostic indicator for cancers.
-
Protein name
Ephrin type-B receptor 4
-
Protein short names
EPHB4; HTK; MYK1; AI042935; MDK2; TYRO11
-
Uniprot ID
Q96L35
-
Gene Name
EPHB4; HTK; MYK1; TYRO11
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Ala 539) of human EphB4 (NP_004435.3) precursor was expressed with the fused Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Human
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant human EphB4/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein after removal of the signal peptide. The reduced monomer consists of 762 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 83.8 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the rhEphB4/Fc monomer migrates as an approximately 105-115 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions.
-
Purity
> 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Activity
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human EFNB2 at 2 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human EphB4-Fc with a linear ranger of 1.56-12.5 ng/ml.
-
Validations
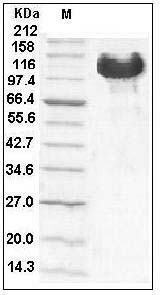
Human EphB4 / HTK Protein (Fc Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
