-
Product Name
GRIN2B Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to GRIN2B
-
Tested applications
WB, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
GRIN2B antibody; EIEE27 antibody; GluN2B antibody; MRD6 antibody; NMDAR2B antibody; NR2B antibody; hNR3 antibody; glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2B antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 1400 to the C-terminus of human GRIN2B (NP_000825.2).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IF 1:50 - 1:200 -
Validations
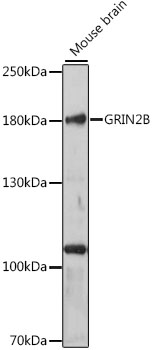
Western blot - GRIN2B Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of mouse brain, using GRIN2B antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 90s.
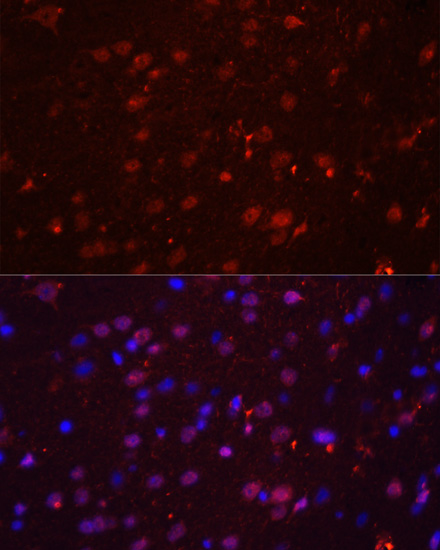
Immunofluorescence - GRIN2B Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of rat brain using GRIN1 antibody at dilution of 1:100. Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
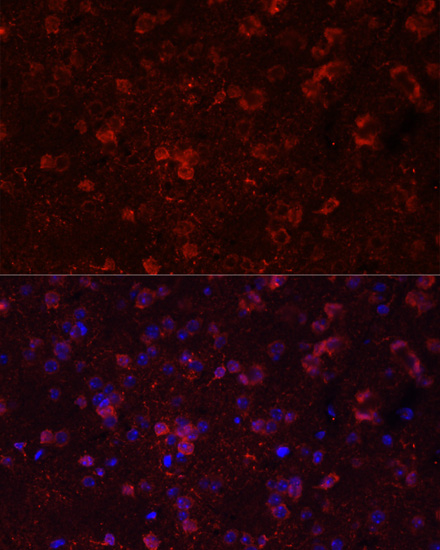
Immunofluorescence - GRIN2B Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of mouse brain using GRIN1 antibody at dilution of 1:100. Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
-
Background
Component of NMDA receptor complexes that function as heterotetrameric, ligand-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Channel activation requires binding of the neurotransmitter glutamate to the epsilon subunit, glycine binding to the zeta subunit, plus membrane depolarization to eliminate channel inhibition by Mg(2+). Sensitivity to glutamate and channel kinetics depend on the subunit composition. In concert with DAPK1 at extrasynaptic sites, acts as a central mediator for stroke damage. Its phosphorylation at Ser-1303 by DAPK1 enhances synaptic NMDA receptor channel activity inducing injurious Ca2+ influx through them, resulting in an irreversible neuronal death. Contributes to neural pattern formation in the developing brain. Plays a role in long-term depression (LTD) of hippocampus membrane currents and in synaptic plasticity (By similarity).
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
