-
Product Name
FABP4 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
FABP4 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IF detected in mouse adipose, HUVEC cells. Positive IHC detected in human cervix tissue, human skin tissue. Positive WB detected in rat skeletal muscle tissue, human heart tissue, mouse skeletal muscle tissue, mouse small intestine tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 15 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
A FABP antibody; AFABP antibody; ALBP antibody; aP2 antibody; FABP4 antibody; Fatty acid binding protein 4 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of FABP4 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_001442). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
IF: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
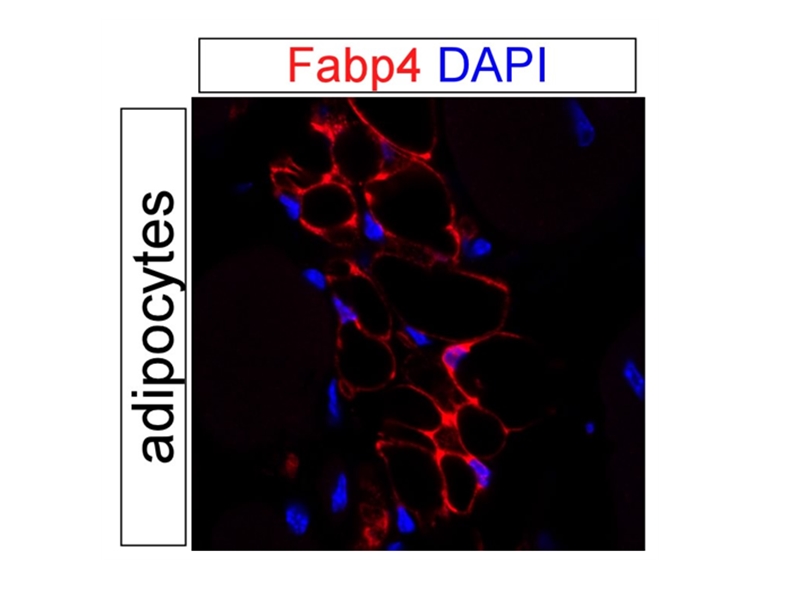
IF result of anti-FABP4 (Catalog No:110439, 1:500) with PFA fixed mouse adipose tissue by Dr. Daniel Kopinke.
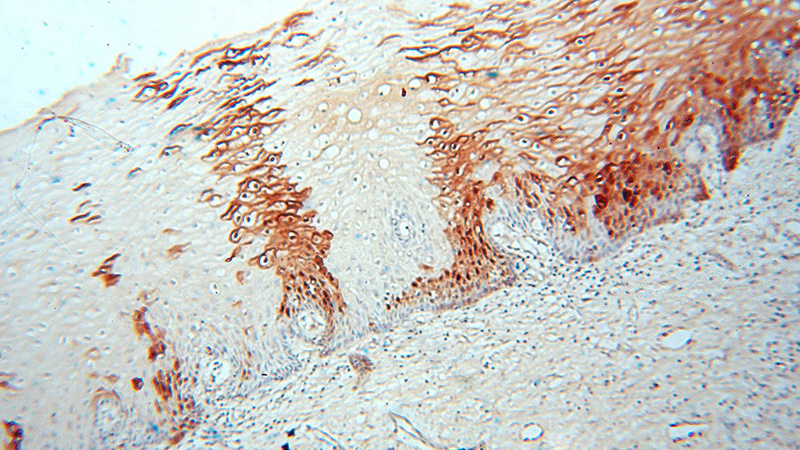
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human cervix using Catalog No:110439(FABP4 antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)
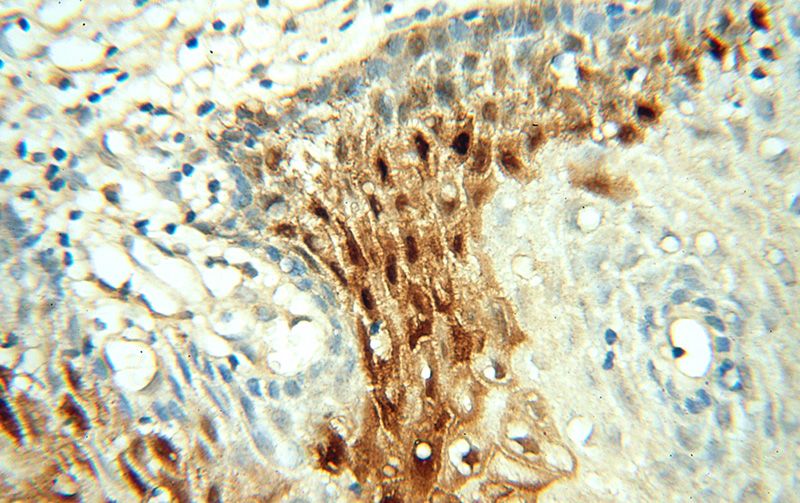
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human cervix using Catalog No:110439(FABP4 antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
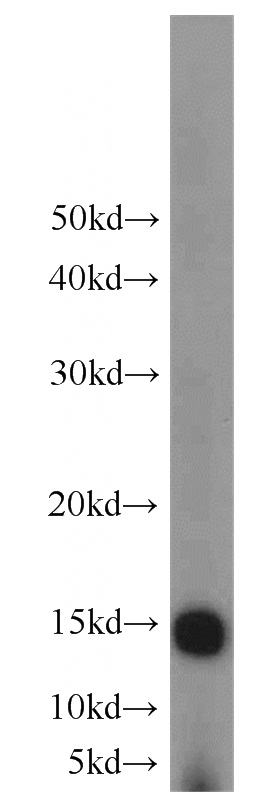
rat skeletal muscle tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:110439(FABP4 antibody) at dilution of 1:600
-
Background
Fatty acid binding protein (FABP) 4 is a member of the FABP family which abundantly expressed, fatty acid carrier proteins. FABPs are capable of binding a variety of hydrophobic molecules such as long-chain fatty acids and are important for their uptake and intracellular trafficking. It was first identified as an adipocyte-specific protein, important for the maintenance of lipid and glucose metabolism. It is also detected in macrophages, where it participates in regulating inflammation and cholesterol trafficking via NFκB and PPAR. In more recent studies, FABP4 has been found in a variety of endothelial cells, where it has been identified as a target of VEGF and a regulator of cell proliferation and possibly angiogenesis. Pathologically, FABP4 has been associated with the development of metabolic syndrome, diabetes and cancer and vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaques. FABP4 has been identified as a novel prognostic factor for both adverse cardiovascular events and breast cancer.
-
References
- Peeters W, de Kleijn DP, Vink A. Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein in atherosclerotic plaques is associated with local vulnerability and is predictive for the occurrence of adverse cardiovascular events. European heart journal. 32(14):1758-68. 2011.
- Zhou J, Guo F, Wang G. miR-20a regulates adipocyte differentiation by targeting lysine-specific demethylase 6b and transforming growth factor-β signaling. International journal of obesity (2005). 39(8):1282-91. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
