-
Product Name
Human SerpinI2 (His Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Serpins are the largest and most diverse family of serine protease inhibitors which are involved in a number of fundamental biological processes such as blood coagulation, complement activation, fibrinolysis, angiogenesis, inflammation and tumor suppression and are expressed in a cell-specific manner. Serpins are a group of proteins with similar structures that were first identified as a set of proteins able to inhibit proteases. The acronym serpin was originally coined because many serpins inhibit chymotrypsin-like serine proteases (serine protease inhibitors). Over 1000 serpins have been identified. Serpin-I2, also known as myoepithelium-derived serine protease inhibitor, Pancreas-specific protein TSA2004, Peptidase inhibitor 14, PI14, SERPINI2 and MEPI, is a secreted protein which belongs to the serpin family. It is expressed in pancreas and adipose tissues. SERPINI2 deficiency directly results in the acinar cell apoptosis and malabsorption.
-
Protein name
cDNA FLJ56490, highly similar to Serpin I2
-
Protein short names
MEPI; SERPINI2; 1810006A24RIK; PI14; PANCPIN; SPI14; TSA2004
-
Uniprot ID
O75830
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the human SERPINI2 (NP_006208.1) (Met 1-Leu 405) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Human
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant human SERPINI2 consists of 398 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 45.5 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhSERPINI2 is approximately 45-55 kDa due to glycosylation.
-
Purity
> 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Validations
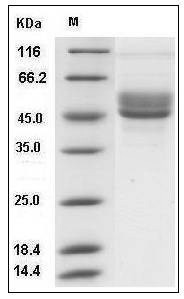
Human SerpinI2 Protein (His Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
