-
Product Name
ATP6V1D antibody
- Documents
-
Description
ATP6V1D Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive FC detected in HeLa cells. Positive IHC detected in human lung cancer tissue. Positive IP detected in mouse lung tissue. Positive WB detected in human brain tissue, mouse lung tissue, mouse skeletal muscle tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 28 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, FC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
ATP6M antibody; ATP6V1D antibody; V ATPase subunit D antibody; V type proton ATPase subunit D antibody; Vacuolar proton pump subunit D antibody; VATD antibody; VMA8 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of ATP6V1D recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_015994). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
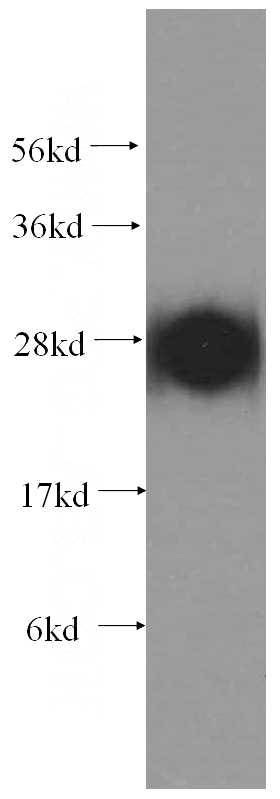
human brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:108310(ATP6V1D antibody) at dilution of 1:500

Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer using Catalog No:108310(ATP6V1D antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 40x lens)

Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer using Catalog No:108310(ATP6V1D antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 10x lens)

IP Result of anti-ATP6V1D (IP:Catalog No:108310, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:108310 1:500) with mouse lung tissue lysate 4000ug.
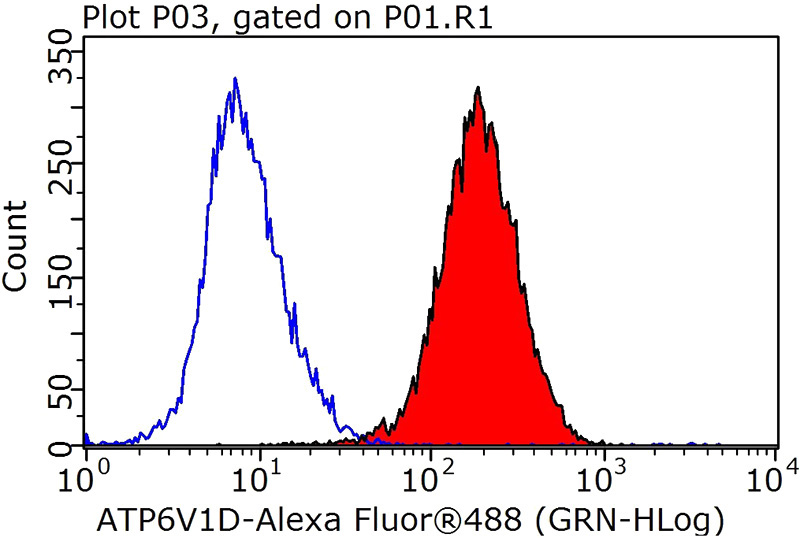
1X10^6 HeLa cells were stained with 0.2ug ATP6V1D antibody (Catalog No:108310, red) and control antibody (blue). Fixed with 90% MeOH blocked with 3% BSA (30 min). Alexa Fluor 488-congugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) with dilution 1:1000.
-
Background
ATP6V1D is also named as ATP6M, VATD(V-type proton ATPase subunit D) and belongs to the V-ATPase D subunit family. ATP6V1D gene has been under strong negative selection during evolution and is highly conserved among mammals, flies, worms, yeast, plants, and bacteria(PMID:11435709). It is responsible for acidifying a variety of intracellular compartments in eukaryotic cells, thus providing most of the energy required for transport processes in the vacuolar system.
-
References
- Sun D, Cheng Y, Zhou D. Quantitative proteome of medulla oblongata in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Journal of proteome research. 12(1):390-5. 2013.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
