-
Product Name
Anti-Alkaline Phosphatase (7G5) Mouse antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Alkaline Phosphatase (7G5) Mouse monoclonal antibody
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC-P, FC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human
-
Isotype
Mouse IgG1
-
Preparation
Antigen: Purified recombinant fragment of human ALPL expressed in E. Coli.
-
Clonality
Monoclonal
-
Formulation
Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide
-
Storage instructions
Store at 4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
-
Applications
WB: 1/500 - 1/2000
IHC: 1/200 - 1/1000
FC: 1/200 - 1/400
ELISA: 1/10000
-
Validations
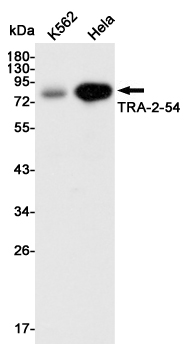
Western blot detection of TRA-2-54 in K562 and Hela cell lysates using TRA-2-54 mouse mAb (1:3000 diluted).Predicted band size:57KDa.Observed band size:80KDa.
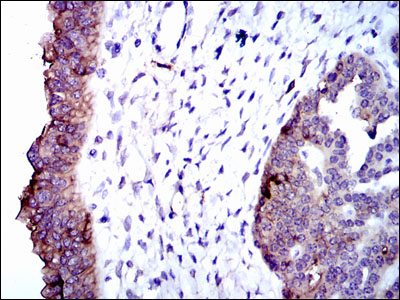
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded ovarian cancer tissues using TRA-2-54 mouse mAb with DAB staining.
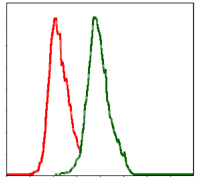
Flow cytometric analysis of MCF-7 cells using TRA-2-54 mouse mAb (green) and negative control (red).
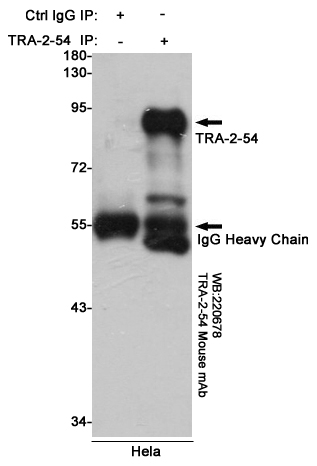
Immunoprecipitation analysis of Hela cell lysates using TRA-2-54 mouse mAb.
-
Background
Swiss-Prot Acc.P05186.There are at least four distinct but related alkaline phosphatases: intestinal, placental, placental-like, and liver/bone/kidney (tissue non-specific). The first three are located together on chromosome 2, while the tissue non-specific form is located on chromosome 1. The product of this gene is a membrane bound glycosylated enzyme that is not expressed in any particular tissue and is, therefore, referred to as the tissue-nonspecific form of the enzyme. The exact physiological function of the alkaline phosphatases is not known. A proposed function of this form of the enzyme is matrix mineralization; however, mice that lack a functional form of this enzyme show normal skeletal development. This enzyme has been linked directly to hypophosphatasia, a disorder that is characterized by hypercalcemia and includes skeletal defects. The character of this disorder can vary, however, depending on the specific mutation since this determines age of onset and severity of symptoms. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described.
-
References
- Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth as an alternative cell source in bio-root regeneration
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
