-
Product Name
ADAR Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to ADAR
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
ADAR antibody; ADAR1 antibody; AGS6 antibody; DRADA antibody; DSH antibody; DSRAD antibody; G1P1 antibody; IFI-4 antibody; IFI4 antibody; K88DSRBP antibody; P136 antibody; adenosine deaminase, RNA specific antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 150-250 of human ADAR (NP_001102.2).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:50 - 1:200
IF 1:50 - 1:200 -
Validations
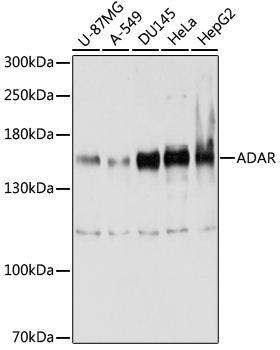
Western blot - ADAR Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using ADAR antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Enhanced Kit .Exposure time: 20s.
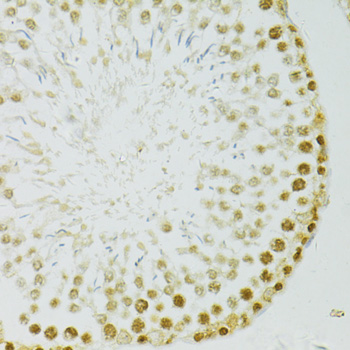
Immunohistochemistry - ADAR Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat testis using ADAR antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
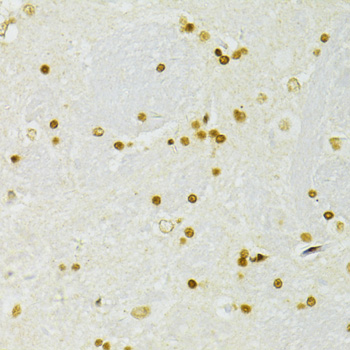
Immunohistochemistry - ADAR Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat brain using ADAR antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
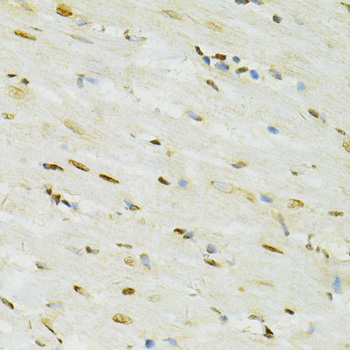
Immunohistochemistry - ADAR Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat heart using ADAR antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
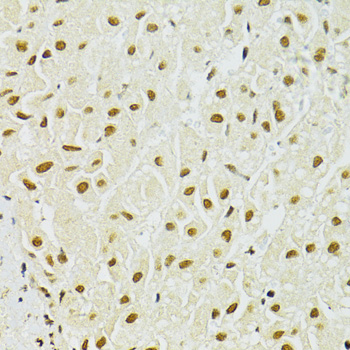
Immunohistochemistry - ADAR Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver using ADAR antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
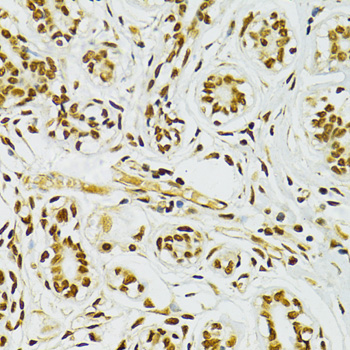
Immunohistochemistry - ADAR Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer using ADAR antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
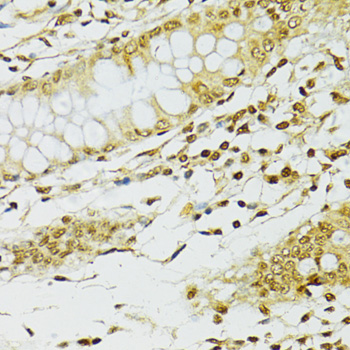
Immunohistochemistry - ADAR Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human stomach using ADAR antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
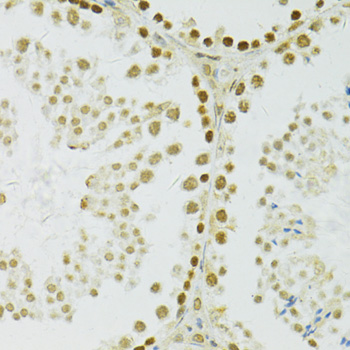
Immunohistochemistry - ADAR Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse testis using ADAR antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
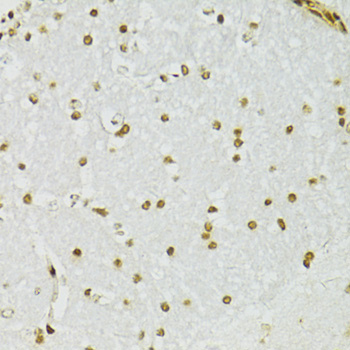
Immunohistochemistry - ADAR Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse brain using ADAR antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
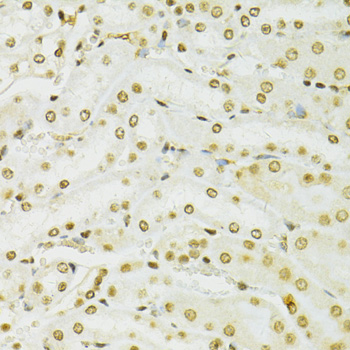
Immunohistochemistry - ADAR Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse kidney using ADAR antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
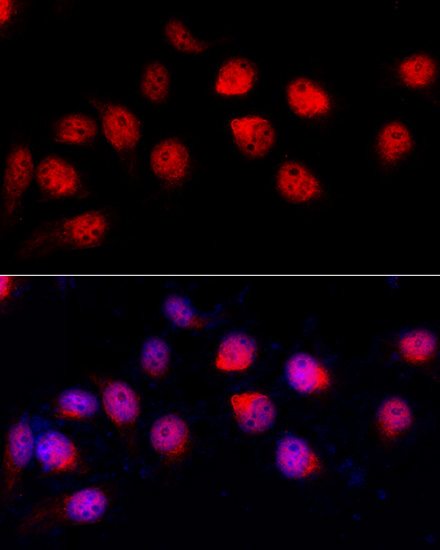
Immunofluorescence - ADAR Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells using ADAR antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens). Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
-
Background
Catalyzes the hydrolytic deamination of adenosine to inosine in double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) referred to as A-to-I RNA editing. This may affect gene expression and function in a number of ways that include mRNA translation by changing codons and hence the amino acid sequence of proteins; pre-mRNA splicing by altering splice site recognition sequences; RNA stability by changing sequences involved in nuclease recognition; genetic stability in the case of RNA virus genomes by changing sequences during viral RNA replication; and RNA structure-dependent activities such as microRNA production or targeting or protein-RNA interactions. Can edit both viral and cellular RNAs and can edit RNAs at multiple sites (hyper-editing) or at specific sites (site-specific editing). Its cellular RNA substrates include: bladder cancer-associated protein (BLCAP), neurotransmitter receptors for glutamate (GRIA2) and serotonin (HTR2C) and GABA receptor (GABRA3). Site-specific RNA editing of transcripts encoding these proteins results in amino acid substitutions which consequently alters their functional activities. Exhibits low-level editing at the GRIA2 Q/R site, but edits efficiently at the R/G site and HOTSPOT1. Its viral RNA substrates include: hepatitis C virus (HCV), vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), measles virus (MV), hepatitis delta virus (HDV), and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). Exhibits either a proviral (HDV, MV, VSV and HIV-1) or an antiviral effect (HCV) and this can be editing-dependent (HDV and HCV), editing-independent (VSV and MV) or both (HIV-1). Impairs HCV replication via RNA editing at multiple sites. Enhances the replication of MV, VSV and HIV-1 through an editing-independent mechanism via suppression of EIF2AK2/PKR activation and function. Stimulates both the release and infectivity of HIV-1 viral particles by an editing-dependent mechanism where it associates with viral RNAs and edits adenosines in the 5'UTR and the Rev and Tat coding sequence. Can enhance viral replication of HDV via A-to-I editing at a site designated as amber/W, thereby changing an UAG amber stop codon to an UIG tryptophan (W) codon that permits synthesis of the large delta antigen (L-HDAg) which has a key role in the assembly of viral particles. However, high levels of ADAR1 inhibit HDV replication.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
