-
Product Name
ACSL4/FACL4 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
ACSL4/FACL4 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IP detected in COLO 320 cells. Positive WB detected in HepG2 cells, HEK-293 cells. Positive IHC detected in human placenta tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 79 kDa,74 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
ACS4 antibody; ACSL4 antibody; FACL4 antibody; LACS 4 antibody; LACS4 antibody; MRX63 antibody; MRX68 antibody
- Immunogen
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of ACSL4/FACL4 recombinant protein (Accession Number: XM_047441918). Purification method: Antigen Affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:500-1:5000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
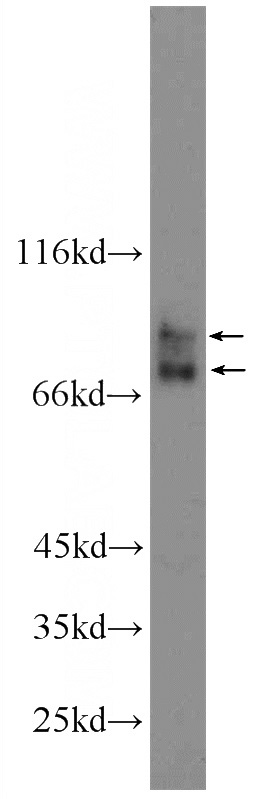
HepG2 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:107697(ACSL4 Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
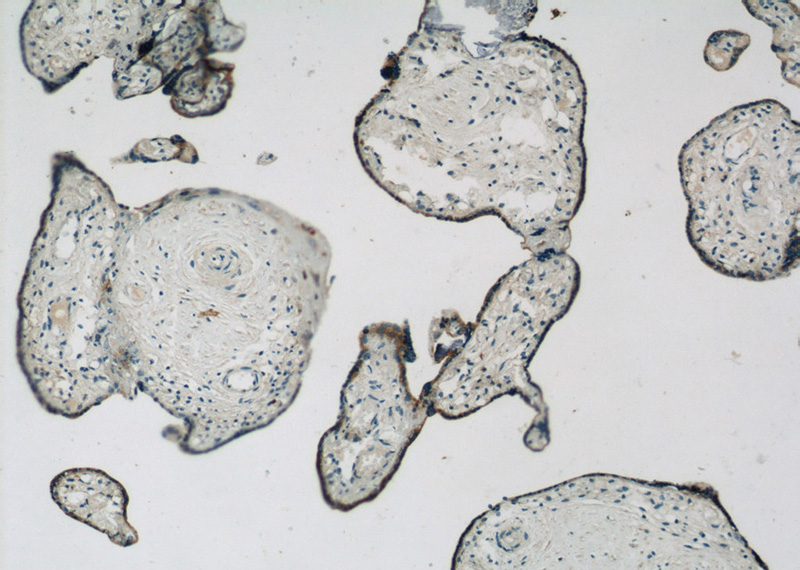
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human placenta slide using Catalog No:107697(ACSL4 Antibody) at dilution of 1:50
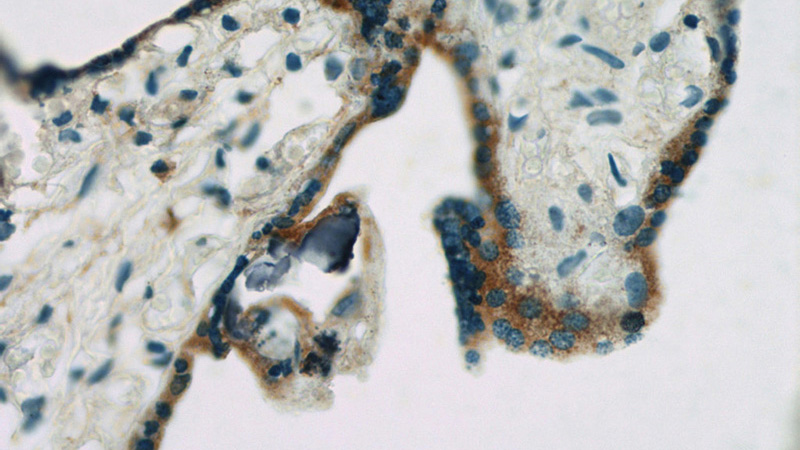
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human placenta slide using Catalog No:107697(ACSL4 Antibody) at dilution of 1:50
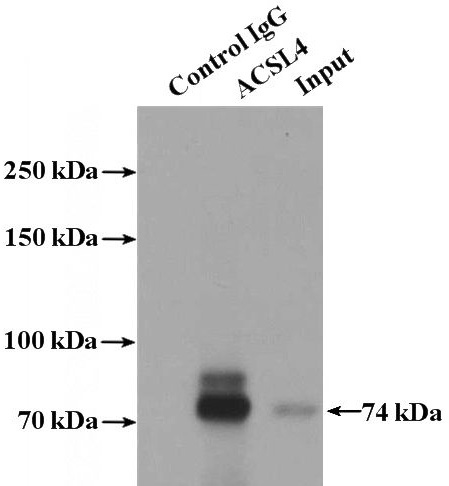
IP Result of anti-ACSL4 (IP:Catalog No:107697, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:107697 1:1000) with COLO 320 cells lysate 2000ug.
-
Background
ACSL4 represents acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4
-
References
- Cui M, Xiao Z, Sun B. Involvement of cholesterol in hepatitis B virus X protein-induced abnormal lipid metabolism of hepatoma cells via up-regulating miR-205-targeted ACSL4. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 445(3):651-5. 2014.
- Saka HA, Thompson JW, Chen YS. Chlamydia trachomatis Infection Leads to Defined Alterations to the Lipid Droplet Proteome in Epithelial Cells. PloS one. 10(4):e0124630. 2015.
- Ye X, Zhang Y, He B, Meng Y, Li Y, Gao Y. Quantitative proteomic analysis identifies new effectors of FOXM1 involved in breast cancer cell migration. International journal of clinical and experimental pathology. 8(12):15836-44. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
