-
Product Name
ACC1 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
ACC1 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human skeletal muscle tissue, human kidney tissue. Positive IF detected in HeLa cells. Positive WB detected in HeLa cells, HEK-293 cells, human brain tissue, PC-3 cells, rat brain tissue. Positive IP detected in HeLa cells. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 260-270 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
ACAC antibody; ACACA antibody; ACC antibody; ACC1 antibody; ACCA antibody; Acetyl CoA carboxylase 1 antibody
- Immunogen
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of ACC1 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_198834). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:2000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
IF: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
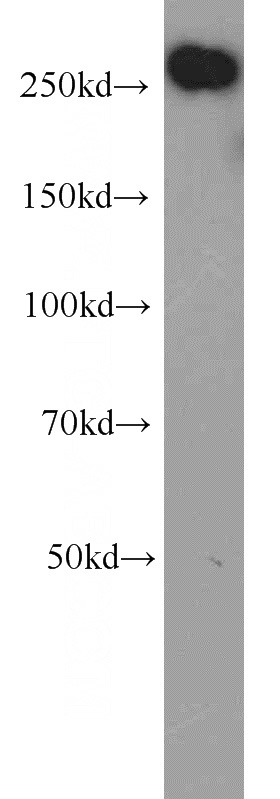
HeLa cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:107732(ACACA antibody) at dilution of 1:500
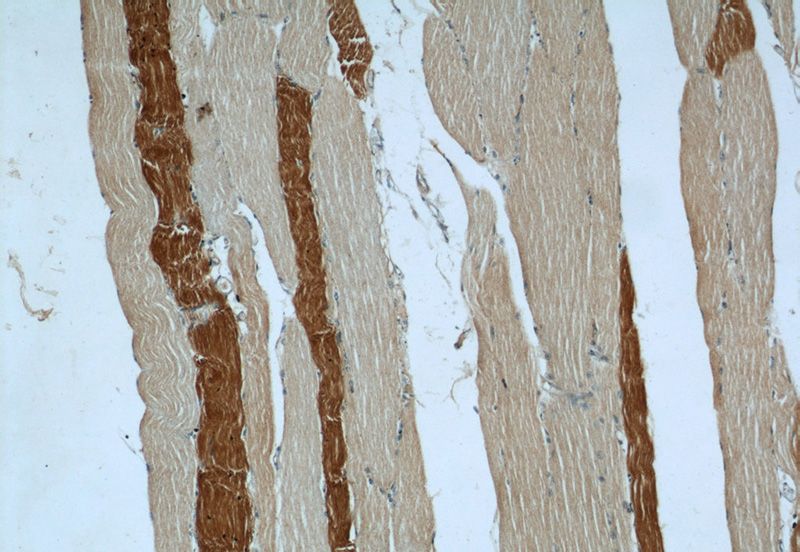
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human skeletal muscle using Catalog No:107732(ACACA antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)
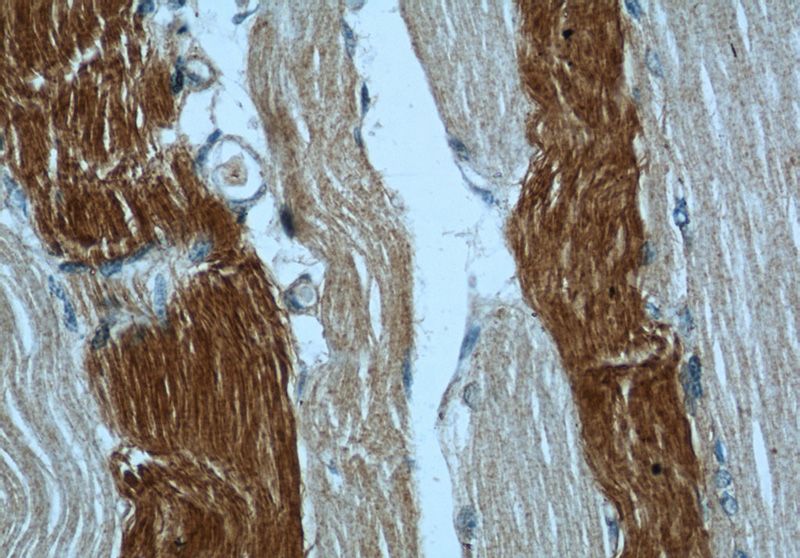
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human skeletal muscle using Catalog No:107732(ACACA antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
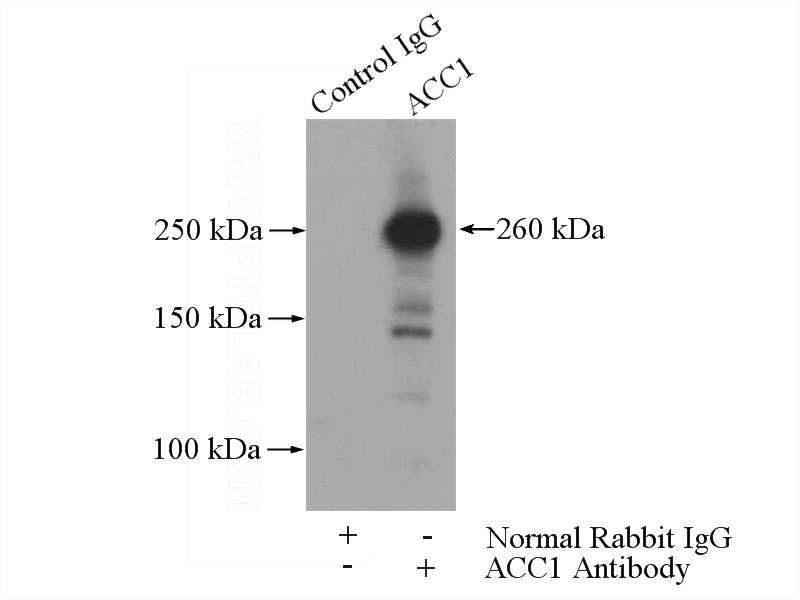
IP Result of anti-ACC (IP:Catalog No:107732, 5ug; Detection:Catalog No:107732 1:500) with HeLa cells lysate 2800ug.
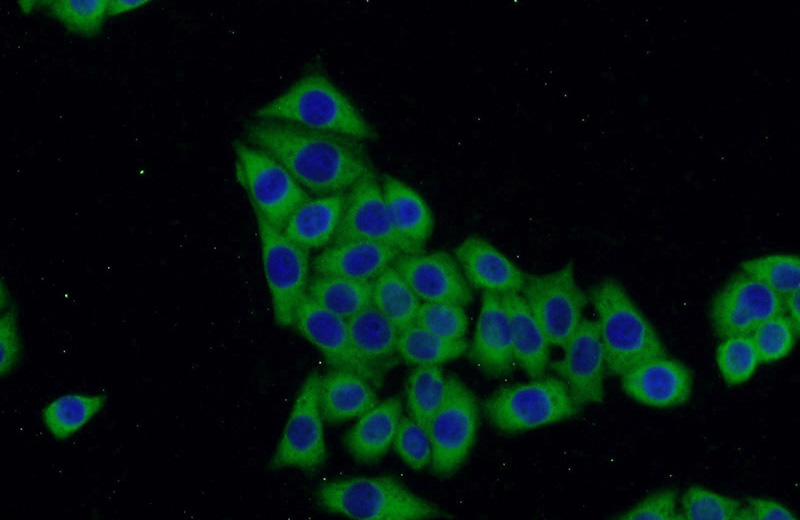
Immunofluorescent analysis of HeLa cells using Catalog No:107732(ACC Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 and Alexa Fluor 488-congugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L)
-
Background
ACACA(Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1, ACC), also named as ACAC, ACC1 and ACCA, belongs to the biotin containing enzyme family. It catalyzes the synthesis of malonyl-CoA, which is an intermediate substrate playing a pivotal role in the regulation of fatty acid metabolism and energy production. ACACA is involved in the biosynthesis of fatty acids, and malonyl-CoA produced is used as a building block to extend the chain length of fatty acids by fatty acid synthase (FAS)(PMID:19900410). It has 4 isoforms produced by alternative promoter usage with the molecular weight between 260 kDa and 270 kDa.
-
References
- Wang MD, Wu H, Fu GB. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase α promotion of glucose-mediated fatty acid synthesis enhances survival of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice and patients. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2015.
- Cai D, Wang J, Jia Y. Gestational dietary betaine supplementation suppresses hepatic expression of lipogenic genes in neonatal piglets through epigenetic and glucocorticoid receptor-dependent mechanisms. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 1861(1):41-50. 2016.
- Wang MD, Wu H, Huang S. HBx regulates fatty acid oxidation to promote hepatocellular carcinoma survival during metabolic stress. Oncotarget. 2016.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
