-
Product Name
WDR5 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
WDR5 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in NIH/3T3 cells, HT-1080 cells, human testis tissue. Positive IHC detected in human brain. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 36kd
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
WDR5 antibody; BIG3 antibody; BMP2 induced 3 kb gene protein antibody; WD repeat containing protein 5 antibody; SWD3 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of WDR5 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_001384415). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations

NIH/3T3 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:116871(WDR5 antibody) at dilution of 1:500
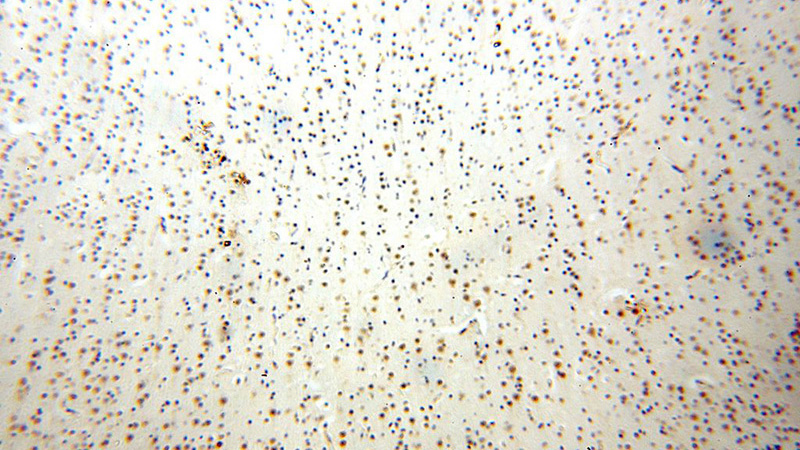
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human brain using Catalog No:116871(WDR5 antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 10x lens)
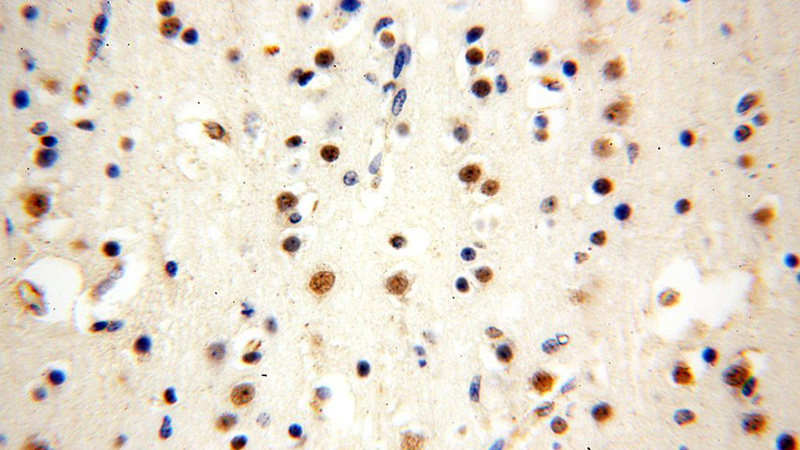
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human brain using Catalog No:116871(WDR5 antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 40x lens)
-
Background
The WDR5 antibody targets the WD repeat protein domain 5 (WDR5), a member of the WD40 repeat protein family in humans. The WDR5 protein is a core member of the mammalian trithorax complex and, like the rest of the WD40 repeat protein family, is primarily involved in diverse cellular processes. WDR5 is identified as a methyl Lys-4 H3-specific-binding protein, however it is known to interact with the Mixed Lineage Leukemia (MLL) protein at the same site for histone H3 tri-methylation(PMID:18840606). Recently, the WDR5 protein has been shown to regulate embryonic stem cell self-renewal, and an increased expression of WDR5 has been found to efficiently induce the formation of pluripotent stem cells (PMID:21477851). WDR5 is also shown to accelerate osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation(PMID:16730692 ).
-
References
- Ma P, Pan H, Montgomery RL, Olson EN, Schultz RM. Compensatory functions of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and HDAC2 regulate transcription and apoptosis during mouse oocyte development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109(8):E481-9. 2012.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
