-
Product Name
UHMK1 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
UHMK1 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human prostate cancer tissue. Positive WB detected in mouse thymus tissue, mouse brain tissue. Positive IP detected in mouse brain tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 47kd
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
KIS antibody; Kist antibody; U2AF homology motif kinase 1 antibody; UHMK1 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of UHMK1 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_144624). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations

mouse thymus tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:116562(UHMK1 antibody) at dilution of 1:500

Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human prostate cancer using Catalog No:116562(UHMK1 antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)
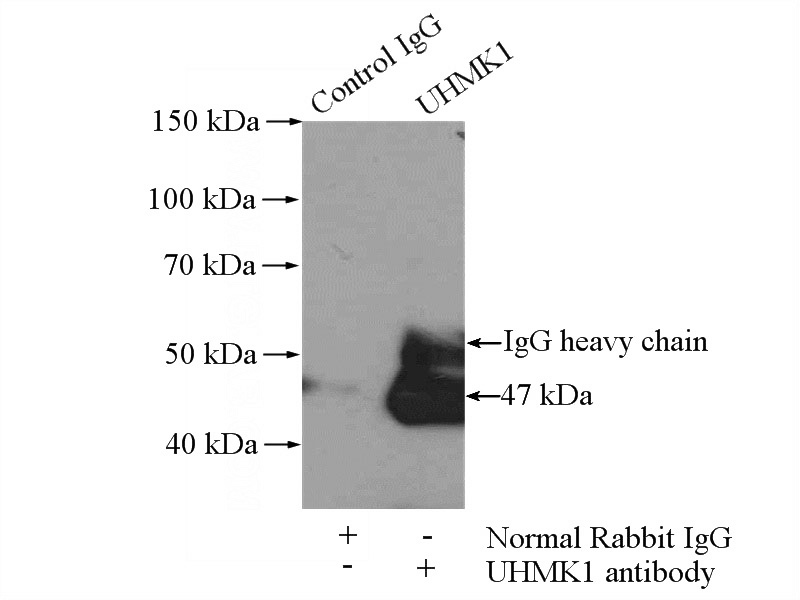
IP Result of anti-UHMK1 (IP:Catalog No:116562, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:116562 1:500) with mouse brain tissue lysate 2640ug.
-
Background
UHMK1, also named as KIS, or KIST, is a 419 amino acid protein, which contains one RRM (RNA recognition motif) domain, one protein kinase domain, and belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. UHMK1 is widely expressed, with highest levels in skeletal muscle, kidney, placenta and peripheral blood leukocytes. UHMK1 localizes in the nucleus and upon serum stimulation, phosphorylating CDKN1B/p27Kip1, thus controlling CDKN1B subcellular location and cell cycle progression in G1 phase. UHMK1 may be involved in trafficking and/or processing of RNA and may have a role in the developing nervous system and the adult brain.
-
References
- Rowe DD, Leonardo CC, Hall AA. Cord blood administration induces oligodendrocyte survival through alterations in gene expression. Brain research. 1366:172-88. 2010.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
