-
Product Name
UBD Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to UBD
-
Tested applications
WB, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse
-
Alternative names
UBD antibody; FAT10 antibody; GABBR1 antibody; UBD-3 antibody; ubiquitin D antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-165 of human UBD (NP_006389.2).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IF 1:50 - 1:200 -
Validations
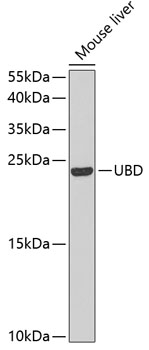
Western blot - UBD Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of mouse liver, using UBD antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 60s.
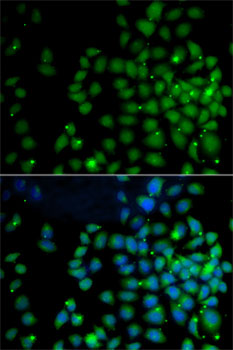
Immunofluorescence - UBD Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of A-549 cells using UBD antibody . Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
-
Background
Ubiquitin-like protein modifier which can be covalently attached to target protein and subsequently leads to their degradation by the 26S proteasome, in a NUB1-dependent manner. Probably functions as a survival factor. Conjugation ability activated by UBA6. Promotes the expression of the proteasome subunit beta type-9 (PSMB9/LMP2). Regulates TNF-alpha-induced and LPS-mediated activation of the central mediator of innate immunity NF-kappa-B by promoting TNF-alpha-mediated proteasomal degradation of ubiquitinated-I-kappa-B-alpha. Required for TNF-alpha-induced p65 nuclear translocation in renal tubular epithelial cells (RTECs). May be involved in dendritic cell (DC) maturation, the process by which immature dendritic cells differentiate into fully competent antigen-presenting cells that initiate T-cell responses. Mediates mitotic non-disjunction and chromosome instability, in long-term in vitro culture and cancers, by abbreviating mitotic phase and impairing the kinetochore localization of MAD2L1 during the prometaphase stage of the cell cycle. May be involved in the formation of aggresomes when proteasome is saturated or impaired. Mediates apoptosis in a caspase-dependent manner, especially in renal epithelium and tubular cells during renal diseases such as polycystic kidney disease and Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated nephropathy (HIVAN).
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
