-
Product Name
TIMELESS antibody
- Documents
-
Description
TIMELESS Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human spleen, human brain, human heart, human kidney, human ovary, human placenta, human testis. Positive WB detected in HeLa cells, A549 cells, NIH/3T3 cells. Positive IP detected in mouse testis tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 140-150 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
FLJ12640 antibody; FLJ20714 antibody; hTIM antibody; Protein timeless homolog antibody; TIM antibody; TIM1 antibody; TIMELESS antibody; timeless homolog (Drosophila) antibody; TIMELESS1 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of TIMELESS recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_003920). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:500-1:5000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
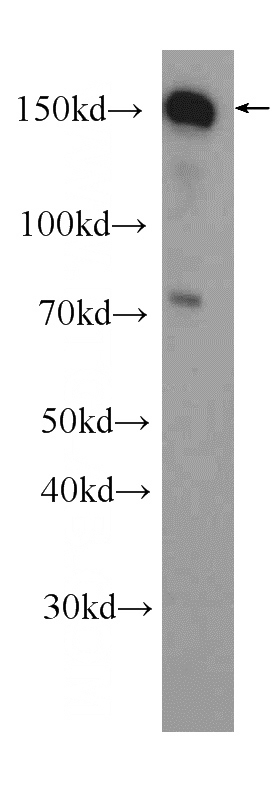
HeLa cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:116128(TIMELESS antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
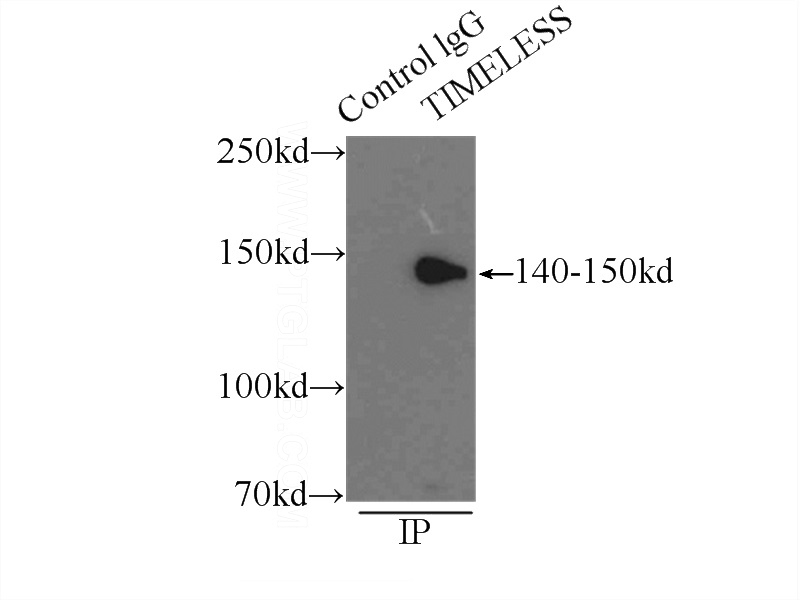
IP Result of anti-TIMELESS (IP:Catalog No:116128, 3ug; Detection:Catalog No:116128 1:1000) with mouse testis tissue lysate 10000ug.
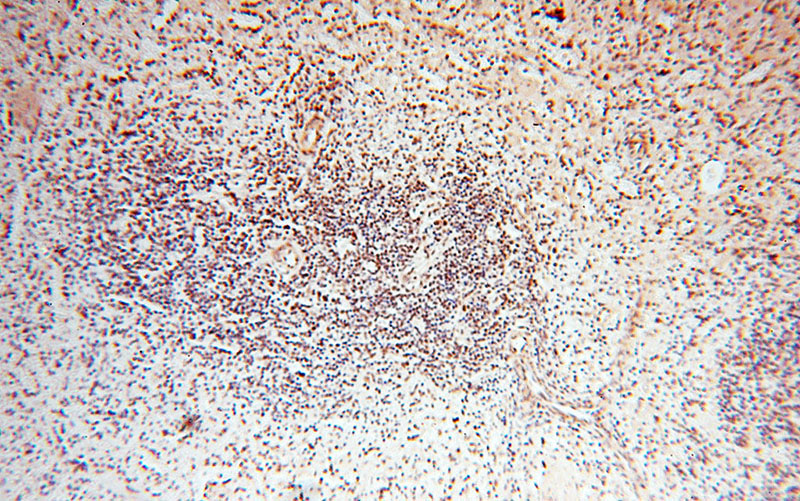
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human spleen using Catalog No:116128(TIMELESS antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)
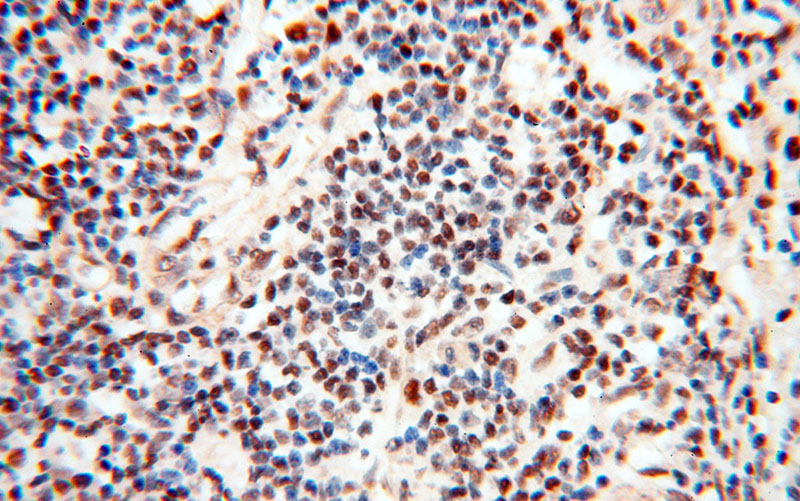
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human spleen using Catalog No:116128(TIMELESS antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
-
Background
TIMELESS1 (TIM1) gene encodes protein timeless homolog belonging to timeless family. TIM1 is localized in nucleus and regulated by cell cycle. It expresses high levels in S, G2 and M phases, and low in G0 and G1 phases. TIM1 is involved in the circadian rhythm autoregulatory loop and is a crucial component of the circadian core oscillator, which includes the CRY proteins, CLocK, NPAS2, etc. It is also involved in cell survival after DNA damage or replication stress and reported to play important role in epithelial cell morphogenesis and formation of branching tubules.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
