-
Product Name
SNAP25 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
SNAP25 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in mouse brain tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 25 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
bA416N4.2 antibody; dJ1068F16.2 antibody; FLJ23079 antibody; RIC 4 antibody; RIC4 antibody; SEC9 antibody; SNAP antibody; SNAP 25 antibody; SNAP25 antibody; SUP antibody; Super protein antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of Recombinant Protein (Accession Number: XM_017028022). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:2000
-
Validations
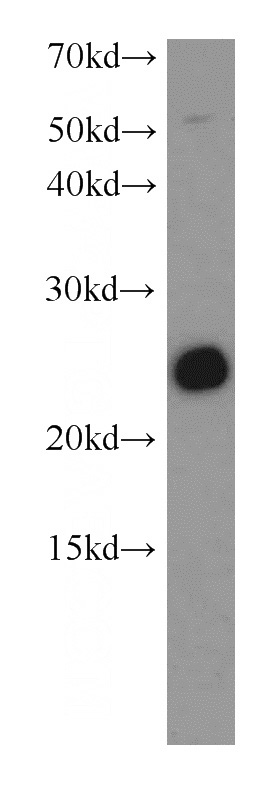
mouse brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:115446(SNAP antibody) at dilution of 1:500
-
Background
The synaptosomal associated protein of 25 kD (SNAP-25) was first identified as a major synaptic protein by Wilson and colleagues. The protein interacts with syntaxin and synaptobrevin through its N-terminal and C-terminal -helical domains. Its palmitoylation domain is located in the middle of the molecule that contains four cysteine residues. Mutation of the cysteines abolishes palmitoylation and membrane binding. Several elegant studies using synaptosome preparations and permeabilized PC12 cells have suggested that SNAP-25 may act in the late post-docking steps of exocytosis. By limited proteolysis and in vitro binding assay, it is proposed that the two helix domains act independently and contribute equally to form the SNARE complex with syntaxin and synaptobrevin. It seems that a major regulatory element is located in the C-terminus of SNAP-25. Removing a 9 amino acid sequence of SNAP-25 inhibited neurosecretion in chromaffin cells. In addition, it has been shown that inhibition of neurosecretion by botulinum toxin E can be rescued by a SNAP-25 C-terminal peptide, probably by initiating the formation of a fusion competent SNARE complex.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
