-
Product Name
SMN antibody
- Documents
-
Description
SMN Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human kidney tissue, human brain tissue, human heart tissue, human lung tissue, human ovary tissue, human placenta tissue, human skin tissue, human spleen tissue, human testis tissue. Positive IF detected in Hela cells, HepG2 cells. Positive WB detected in HEK-293 cells, A549 cells, HeLa cells, HepG2 cells, Jurkat cells, K-562 cells, mouse testis tissue. Positive IP detected in HEK-293. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 38 kDa; 66-70 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, IHC, IF, IP, WB
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
C BCD541 antibody; Component of gems 1 antibody; FLJ76644 antibody; Gemin 1 antibody; SMN antibody; SMN1 antibody; SMN1 antibody; SMN antibody; SMN2 antibody; SMNC antibody; SMNT antibody; Survival motor neuron protein antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of SMN recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_022875). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:500-1:5000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
IF: 1:10-1:100
-
Validations

HEK-293 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:115393(SMN2 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
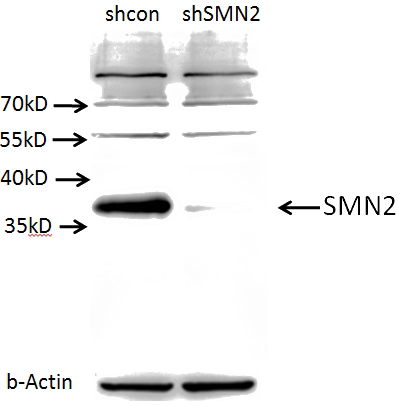
A549 cells (shcontrol and shRNA of SMN) were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:115393 (SMN2 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000. (Data provided by Angran Biotech (www.miRNAlab.com)).
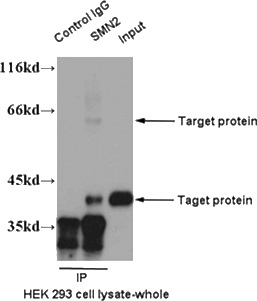
IP result of anti-SMN2(Catalog No:115393 for IP and Detection).
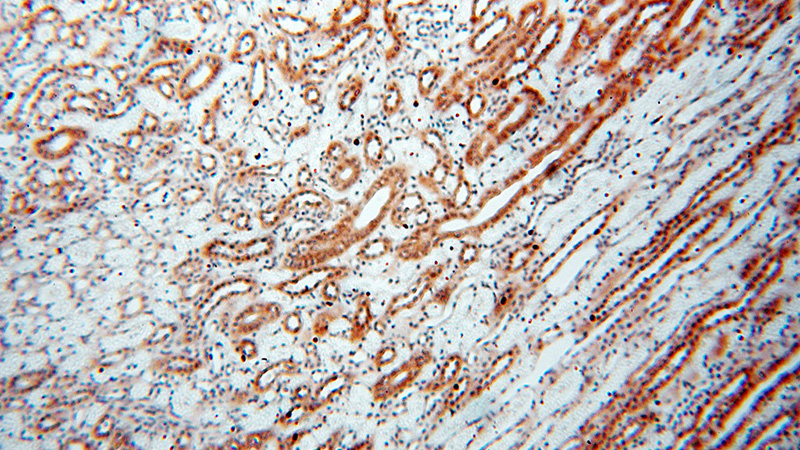
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human kidney using Catalog No:115393(SMN2 antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 10x lens)
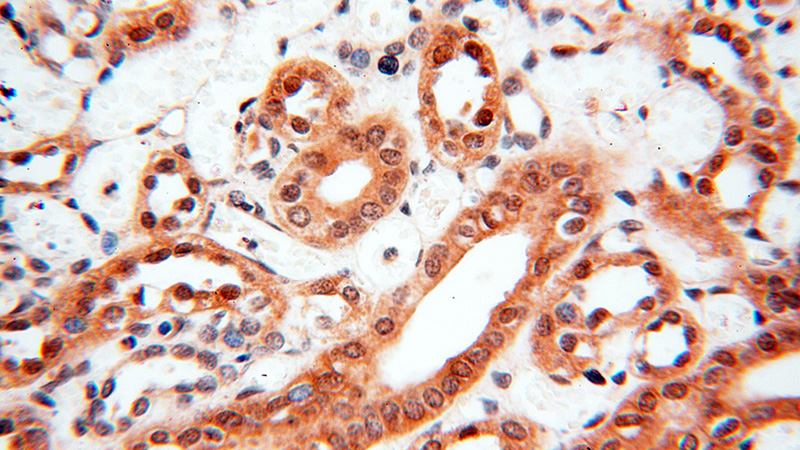
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human kidney using Catalog No:115393(SMN2 antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 40x lens)
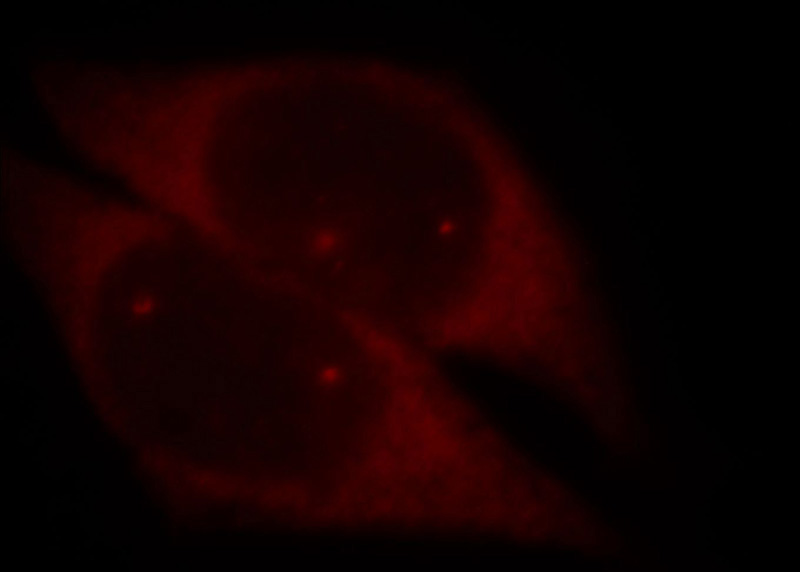
Immunofluorescent analysis of Hela cells, using SMN2 antibody Catalog No:115393 at 1:25 dilution and Rhodamine-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (red).
-
Background
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is an autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disease characterized by loss of anterior horn cells in the spinal cord and concomitant symmetrical muscle weakness and atrophy (PMID: 16364894 ). SMA is caused by deletion or mutations of the survival motor neuron (SMN1) gene. SMA patients lack a functional SMN1 gene, but they possess an intact SMN2 gene, which though nearly identical to SMN1, is only partially functional (PMID: 17355180). A large majority of SMN2 transcripts lack exon 7, resulting in production of a truncated, less stable SMN protein (PMID: 10369862). The level of SMN protein correlates with phenotypic severity of SMA. This antibody, 11708-1-AP, raised against the recombinant full-length human SMN2 protein, recognizes all isoforms of SMN protein.
-
References
- Kobayashi DT, Olson RJ, Sly L. Utility of survival motor neuron ELISA for spinal muscular atrophy clinical and preclinical analyses. PloS one. 6(8):e24269. 2011.
- Crawford TO, Paushkin SV, Kobayashi DT. Evaluation of SMN protein, transcript, and copy number in the biomarkers for spinal muscular atrophy (BforSMA) clinical study. PloS one. 7(4):e33572. 2012.
- Steinkellner H, Etzler J, Gmeiner BM, Laccone F. Detection of survival motor neuron protein in buccal cells through electrochemiluminescence-based assay. Assay and drug development technologies. 13(3):167-73. 2015.
- McGovern VL, Iyer CC, Arnold WD. SMN expression is required in motor neurons to rescue electrophysiological deficits in the SMNΔ7 mouse model of SMA. Human molecular genetics. 24(19):5524-41. 2015.
- Iyer CC, McGovern VL, Murray JD. Low levels of Survival Motor Neuron protein are sufficient for normal muscle function in the SMNΔ7 mouse model of SMA. Human molecular genetics. 24(21):6160-73. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
