-
Product Name
RNF34 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to RNF34
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Human
-
Alternative names
RNF34 antibody; CARP-1 antibody; CARP1 antibody; RFI antibody; RIF antibody; RIFF antibody; hRFI antibody; ring finger protein 34 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-220 of human RNF34 (NP_079402.2).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
-
Validations
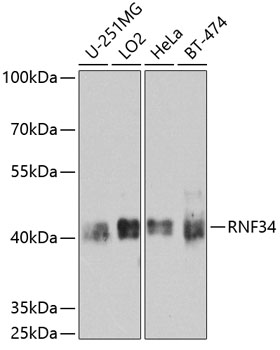
Western blot - RNF34 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using RNF34 antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 90s.
-
Background
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that regulates several biological processes through the ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation of various target proteins. Ubiquitinates the caspases CASP8 and CASP10, promoting their proteasomal degradation, to negatively regulate cell death downstream of death domain receptors in the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis. May mediate 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination of RIPK1 and its subsequent proteasomal degradation thereby indirectly regulating the tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway (Ref.13). Negatively regulates p53/TP53 through its direct ubiquitination and targeting to proteasomal degradation. Indirectly, may also negatively regulate p53/TP53 through ubiquitination and degradation of SFN. Mediates PPARGC1A proteasomal degradation probably through ubiquitination thereby indirectly regulating the metabolism of brown fat cells. Possibly involved in innate immunity, through 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination of NOD1 and its subsequent proteasomal degradation.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
