-
Product Name
Rhesus CD137 / 4-1BB (Fc Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
CD137 (also known as 4-1BB) is a surface co-stimulatory glycoprotein originally described as present on activated T lymphocytes, which belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily. It is expressed mainly on activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and binds to a high-affinity ligand (4-1BBL) expressed on several antigen-presenting cells such as macrophages and activated B cells. Upon ligand binding, 4-1BB is associated with the tumor necrosis factor receptor–associated factors (TRAFs), the adaptor protein which mediates downstream signaling events including the activation of NF-kappaB and cytokine production. 4-1BB signaling either by binding to 4-1BBL or by antibody ligation delivers signals for T-cell activation and growth, as well as monocyte proliferation and B-cell survival, and plays an important role in the amplification of T cell-mediated immune responses. In addition, CD137 and CD137L are expressed in different human primary tumor tissues, suggesting that they may influence the progression of tumors. Crosslinking of CD137 on activated T cells has shown promise in enhancing anti-tumor immune responses in murine models, and agonistic anti-CD137 antibodies are currently being tested in phase I clinical trials.
-
Protein short names
RP23-272N19.6; AI325004; MGC2172; A930040I11RIK; ILA; TNFRSF9; 4-1BB; AA408498; CDW137; CD137; LY63
-
Uniprot ID
F6W5G6
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the rhesus TNFRSF9 (NP_001253057.1) (Met1-Gln186) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Rhesus
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant rhesus TNFRSF9 consists of 401 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 44 kDa.
-
Purity
> 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
Validations
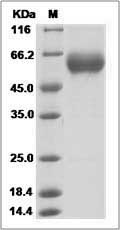
Rhesus CD137 / 4-1BB Protein (Fc Tag)
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
