-
Product Name
RELN antibody
- Documents
-
Description
RELN Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human liver tissue.
-
Tested applications
ELISA, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
PRO1598 antibody; reelin antibody; RELN antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of Peptide (Accession Number: NM_005045). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
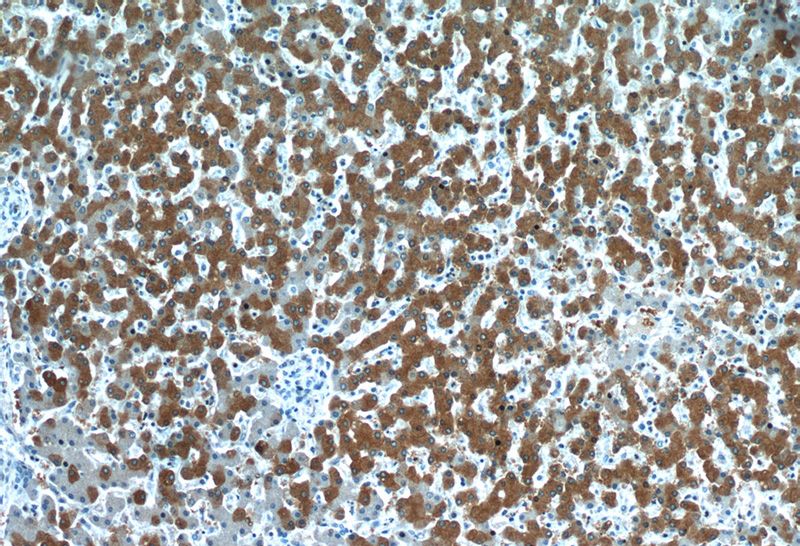
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver slide using Catalog No:114685(RELN Antibody) at dilution of 1:50(under 10x lens)
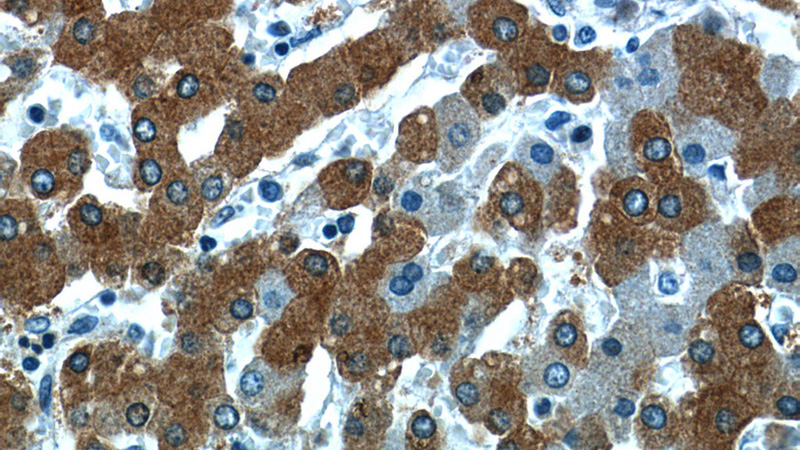
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver slide using Catalog No:114685(RELN Antibody) at dilution of 1:50(under 40x lens)
-
Background
RELN belongs to the reelin family. It is an extracellular matrix serine protease that plays a role in layering of neurons in the cerebral cortex and cerebellum. It is a secreted glycoprotein which is essential for neuronal migration in the cortex. RELN regulates microtubule function in neurons and neuronal migration. It affects migration of sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the spinal cord, where it seems to act as a barrier to neuronal migration. Enzymatic activity is important for the modulation of cell adhesion. Binding to the extracellular domains of lipoprotein receptors VLDLR and ApoER2, RELN induces tyrosine phosphorylation of Dab1 and modulation of Tau phosphorylation. Defects in RELN are the cause of lissencephaly type 2 (LIS2).
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
