-
Product Name
RAD9A Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to RAD9A
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
RAD9A antibody; RAD9 antibody; RAD9 checkpoint clamp component A antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 162-391 of human RAD9A (NP_004575.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:50 - 1:200
IF 1:50 - 1:200 -
Validations
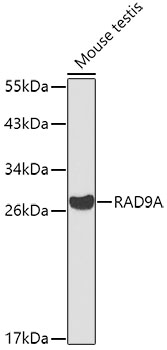
Western blot - RAD9A Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of mouse testis, using RAD9A antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.
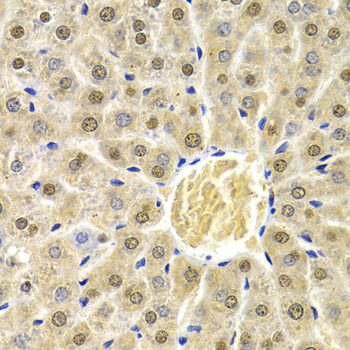
Immunohistochemistry - RAD9A Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat liver using RAD9A antibody at dilution of 1:200 (40x lens).
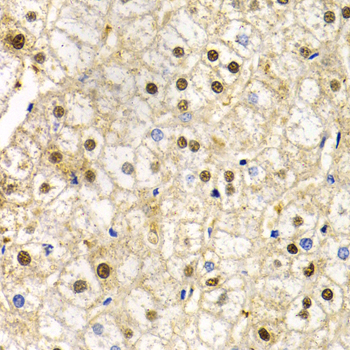
Immunohistochemistry - RAD9A Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver injury using RAD9A antibody at dilution of 1:200 (40x lens).
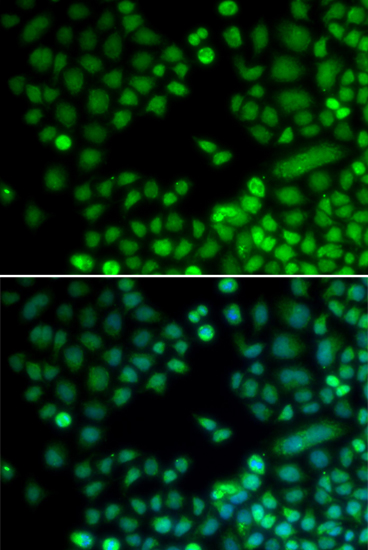
Immunofluorescence - RAD9A Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of MCF-7 cells using RAD9A antibody . Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
-
Background
Component of the 9-1-1 cell-cycle checkpoint response complex that plays a major role in DNA repair. The 9-1-1 complex is recruited to DNA lesion upon damage by the RAD17-replication factor C (RFC) clamp loader complex. Acts then as a sliding clamp platform on DNA for several proteins involved in long-patch base excision repair (LP-BER). The 9-1-1 complex stimulates DNA polymerase beta (POLB) activity by increasing its affinity for the 3'-OH end of the primer-template and stabilizes POLB to those sites where LP-BER proceeds; endonuclease FEN1 cleavage activity on substrates with double, nick, or gap flaps of distinct sequences and lengths; and DNA ligase I (LIG1) on long-patch base excision repair substrates. The 9-1-1 complex is necessary for the recruitment of RHNO1 to sites of double-stranded breaks (DSB) occurring during the S phase. RAD9A possesses 3'->5' double stranded DNA exonuclease activity. Its phosphorylation by PRKCD may be required for the formation of the 9-1-1 complex.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
