-
Product Name
RAB3A antibody
- Documents
-
Description
RAB3A Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IP detected in mouse brain tissue. Positive WB detected in mouse brain tissue. Positive IHC detected in human gliomas tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 25 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
RAB3A antibody; Ras related protein Rab 3A antibody
- Immunogen
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of RAB3A recombinant protein (Accession Number: XM_011528164). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:1000-1:10000
IP: 1:500-1:5000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
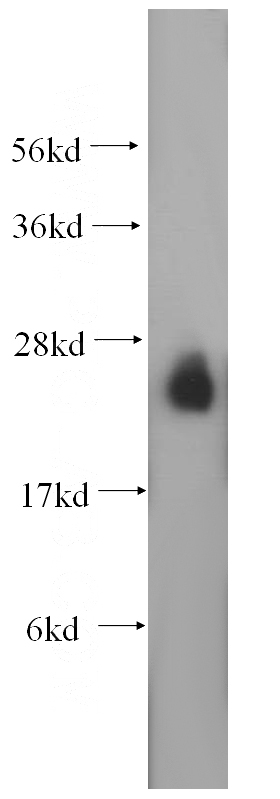
mouse brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:114439(RAB3A antibody) at dilution of 1:1000

Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human gliomas using Catalog No:114439(RAB3A antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 10x lens)

Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human gliomas using Catalog No:114439(RAB3A antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 40x lens)
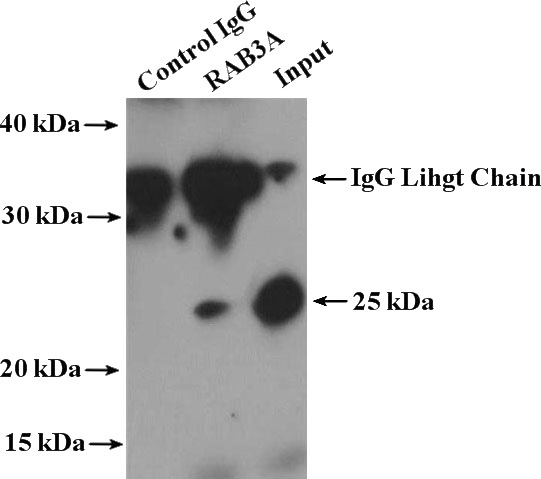
IP Result of anti-RAB3A (IP:Catalog No:114439, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:114439 1:1000) with mouse brain tissue lysate 4000ug.
-
Background
Rab3A is a small G-protein of the Rab family, that is implicated in vesicle fusion and regulated secretion, particularly in neurotransmitter release. Rab3 subfamily small G proteins (Rab3A, Rab3B, Rab3C, and Rab3D) control the regulated exocytosis in neuronal/secretory cells. Rab3A is the most abundant Rab GTPase in brain, where it is associated with synaptic vesicles. Rab3a is believed to modulate secretion efficiency by stimulating vesicle recruitment to sites of exocytosis and/ or by recruiting regulatory molecules to the docking/ fusion machinery.
-
References
- Lakshmana MK, Hayes CD, Bennett SP. Role of RanBP9 on amyloidogenic processing of APP and synaptic protein levels in the mouse brain. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 26(5):2072-83. 2012.
- Wang H, Wang R, Xu S, Lakshmana MK. RanBP9 overexpression accelerates loss of pre and postsynaptic proteins in the APΔE9 transgenic mouse brain. PloS one. 9(1):e85484. 2014.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
