-
Product Name
PROS1 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
PROS1 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human liver tissue. Positive WB detected in human placenta tissue, mouse placenta tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 70 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
PROS antibody; PROS1 antibody; protein S (alpha) antibody; PS21 antibody; PS22 antibody; PS23 antibody; PS24 antibody; PS25 antibody; PSA antibody; Vitamin K dependent protein S antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of PROS1 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_000313). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
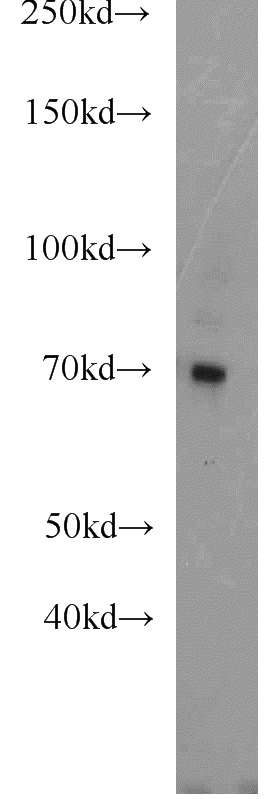
human placenta tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:114219(PROS1 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
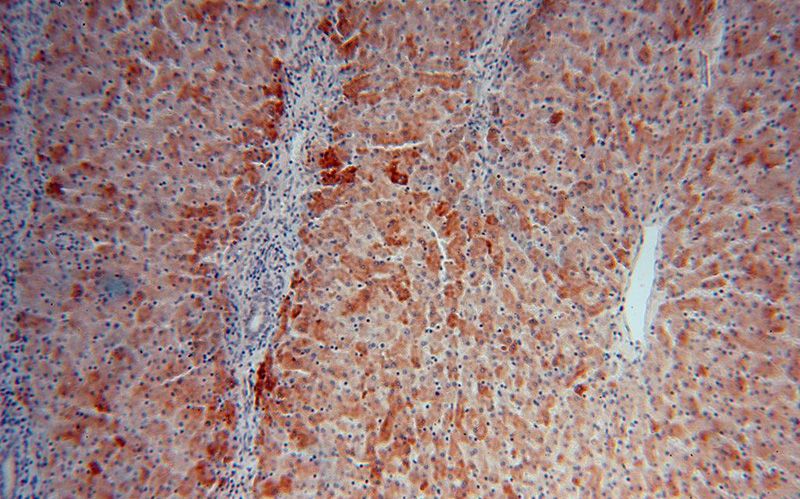
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human liver using Catalog No:114219(PROS1 antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 10x lens)
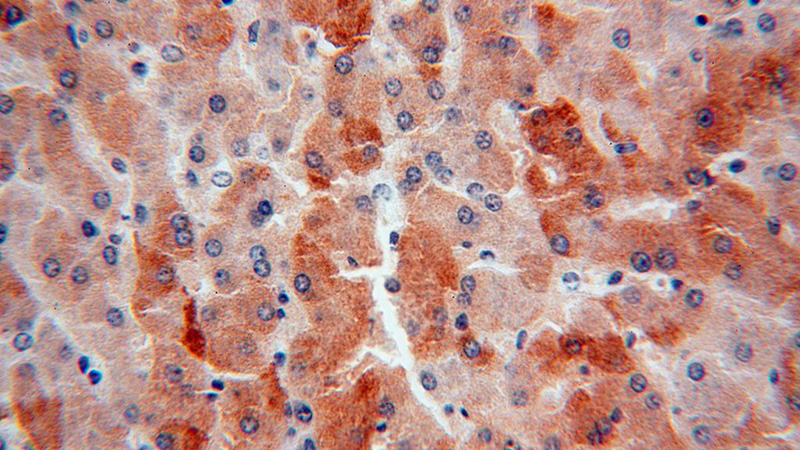
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human liver using Catalog No:114219(PROS1 antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 40x lens)
-
Background
PROS1, also named as Vitamin K-dependent protein S, is a 676 amino acid protein, which contains 4 EGF-like domains, contains one Gla (gamma-carboxy-glutamate) domain and contains 2 laminin G-like domains. PROS1 as a secreted protein platelets alpha granules is expressed in plasma. PROS1 is a cofactor to activated protein C in the degradation of coagulation factors Va and VIIIa and helps to prevent coagulation and stimulating fibrinolysis.
-
References
- Higuchi Y, Kubota T, Koyanagi M, Maeda T, Feldman AM, Makino N. Upregulation of anticoagulant proteins, protein S and tissue factor pathway inhibitor, in the mouse myocardium with cardio-specific TNF-α overexpression. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology. 302(11):H2352-62. 2012.
- Tang L, Jian XR, Hamasaki N. Molecular basis of protein S deficiency in China. American journal of hematology. 88(10):899-905. 2013.
- Wang ZH, Zhao ZJ, Xu K. Hereditary protein S deficiency leads to ischemic stroke. Molecular medicine reports. 12(3):3279-84. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
