-
Product Name
PRKAG2 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to PRKAG2
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
PRKAG2 antibody; AAKG antibody; AAKG2 antibody; CMH6 antibody; H91620p antibody; WPWS antibody; 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit gamma-2 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-328 of human PRKAG2 (NP_077747.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:50 - 1:200 -
Validations
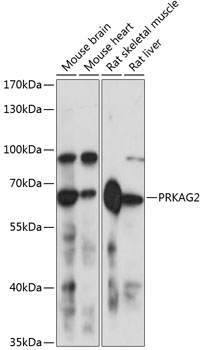
Western blot - PRKAG2 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using PRKAG2 antibody at 1:3000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Enhanced Kit .Exposure time: 1s.
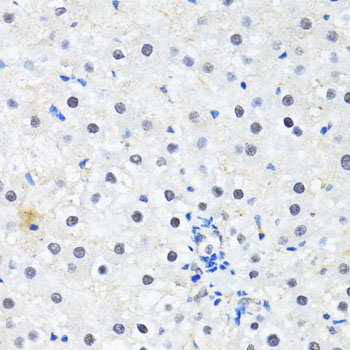
Immunohistochemistry - PRKAG2 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat liver using PRKAG2 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
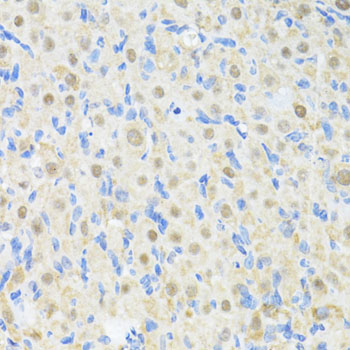
Immunohistochemistry - PRKAG2 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat ovary using PRKAG2 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
-
Background
AMP/ATP-binding subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an energy sensor protein kinase that plays a key role in regulating cellular energy metabolism. In response to reduction of intracellular ATP levels, AMPK activates energy-producing pathways and inhibits energy-consuming processes: inhibits protein, carbohydrate and lipid biosynthesis, as well as cell growth and proliferation. AMPK acts via direct phosphorylation of metabolic enzymes, and by longer-term effects via phosphorylation of transcription regulators. Also acts as a regulator of cellular polarity by remodeling the actin cytoskeleton; probably by indirectly activating myosin. Gamma non-catalytic subunit mediates binding to AMP, ADP and ATP, leading to activate or inhibit AMPK: AMP-binding results in allosteric activation of alpha catalytic subunit (PRKAA1 or PRKAA2) both by inducing phosphorylation and preventing dephosphorylation of catalytic subunits. ADP also stimulates phosphorylation, without stimulating already phosphorylated catalytic subunit. ATP promotes dephosphorylation of catalytic subunit, rendering the AMPK enzyme inactive.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
