-
Product Name
PPAR gamma antibody
- Documents
-
Description
PPAR gamma Mouse Monoclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in A431 cells. Positive IHC detected in human placenta tissue, human colon tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 50-60kd
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
CIMT1 antibody; NR1C3 antibody; PPAR gamma antibody; PPARG antibody; PPARG1 antibody; PPARG2 antibody; PPARgamma antibody
-
Isotype
Mouse IgG1
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of PPAR gamma recombinant protein (Accession Number: XM_011533841). Purification method: Caprylic acid/ammonium sulfate precipitation.
-
Clonality
Monoclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:1000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
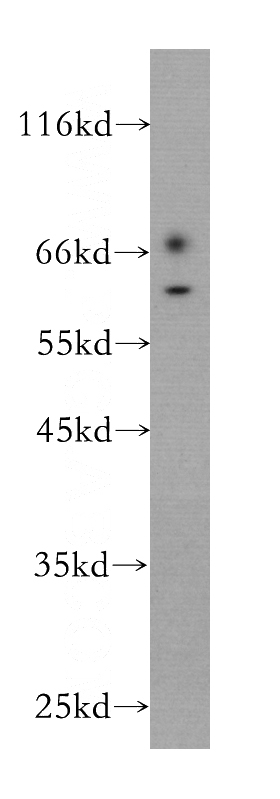
A431 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:107479(PPARG antibody) at dilution of 1:300
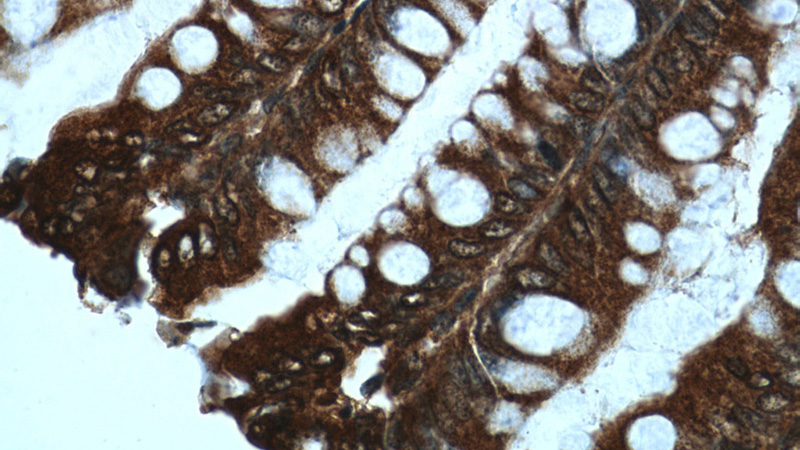
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human colon tissue slide using Catalog No:107479(PPARG Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
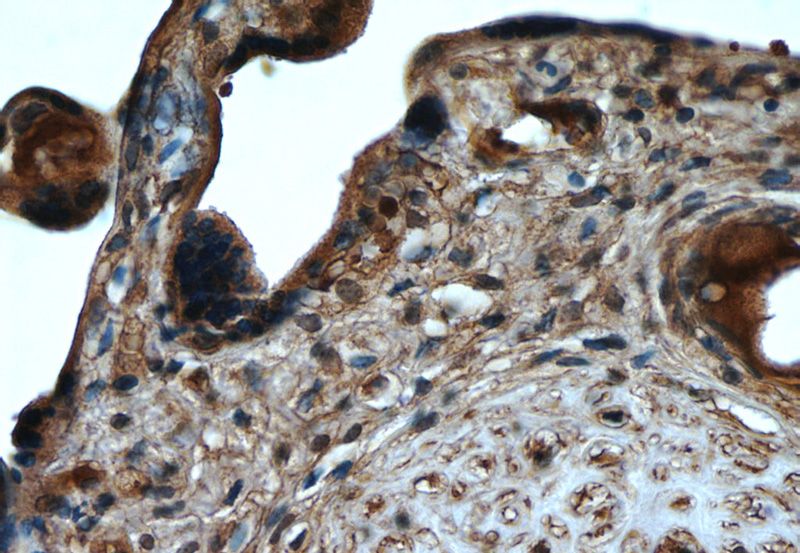
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human placenta tissue slide using Catalog No:107479(PPARG Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
-
Background
Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) are ligand-activated intracellular transcription factors, members of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily (NR), that include estrogen, thyroid hormone receptors, retinoic acid, Vitamin D3 as well as retinoid X receptors (RXRs). The PPAR subfamily consists of three subtypes encoded by distinct genes denoted PPARα (NR1C1), PPARβ/δ (NR1C2) and PPARγ (NR1C3), which are activated by selective ligands. PPARγ, also named as PPARG, contains one nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain and is a receptor that binds peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. It plays an important role in the regulation of lipid homeostasis, adipogenesis, insulin resistance, and development of various organs. Defects in PPARG are the cause of familial partial lipodystrophy type 3 (FPLD3) and may be associated with susceptibility to obesity (OBESITY). Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. Genetic variations in PPARG can be associated with susceptibility to glioma type 1 (GLM1). This antibody is a mouse monoclonal antibody raised against residues near the C terminus of human PPARG.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
